Acute kidney injury: what's the prognosis?
- PMID: 21343898
- PMCID: PMC3547642
- DOI: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.13
Acute kidney injury: what's the prognosis?
Abstract
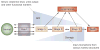
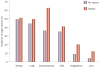
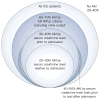
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is common (especially during critical illness), increasing in incidence, and is associated with considerable morbidity and mortality. The Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss, and End-stage renal disease (RIFLE) classification currently provides a standardized estimate of incidence and outcomes from AKI. Despite advances in the understanding of the pathogenesis of human AKI, our ability to assess kidney function is limited and functional impairment poorly correlates with structural injury to the kidneys. Emerging novel biomarkers are, however, likely to further enhance risk stratification, facilitate early diagnosis, enable early enrollment in therapeutic trials, and assess prognosis. Sepsis remains the leading cause of AKI among the critically ill and over the past few years insights into the pathogenesis of AKI in sepsis are beginning to shift attention from renal blood flow to inflammation-mediated organ injury. Emerging evidence suggests that survivors of AKI incur long-term risks for developing chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease compared with those without AKI. Despite decades of research, no specific therapy for AKI other than supportive care currently exists and further work is required to better understand the pathogenesis of AKI during critical illness and to develop novel treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
R. Murugan and J. A. Kellum declare an association with the following company: Baxter. J. A. Kellum declares associations with the following companies: Alere, Abbott Laboratories, Astute Medical, Gambro. See the article online for full details of the relationships.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Our paper 20 years later: from acute renal failure to acute kidney injury--the metamorphosis of a syndrome.Intensive Care Med. 2015 Nov;41(11):1941-9. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-3989-5. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Intensive Care Med. 2015. PMID: 26297119
-
Incidence, risk factors and outcome of acute kidney injury in critically ill children - a developing country perspective.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2017 Feb;37(1):35-41. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2015.1120409. Epub 2016 Jan 9. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2017. PMID: 26752169
-
Urinary biomarkers may provide prognostic information for subclinical acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018 Jun;155(6):2441-2452.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.12.056. Epub 2017 Dec 22. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018. PMID: 29366580
-
Acute kidney injury in critically ill newborns: what do we know? What do we need to learn?Pediatr Nephrol. 2009 Feb;24(2):265-74. doi: 10.1007/s00467-008-1060-2. Epub 2008 Dec 10. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19082634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic biomarkers for the early detection of acute kidney injury.Prilozi. 2012;33(1):27-48. Prilozi. 2012. PMID: 22952093 Review.
Cited by
-
Kidney Injury: Focus on Molecular Signaling Pathways.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(28):4510-4533. doi: 10.2174/0109298673271547231108060805. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38314680 Review.
-
Critical Care Epidemiology and Research in the Face of a Pandemic: An Opportunity in a Crisis.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2020 Apr;24(4):242-244. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23390. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32565633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapamycin protects against gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury via autophagy in mini-pig models.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 8;5:11256. doi: 10.1038/srep11256. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26052900 Free PMC article.
-
[Lung and kidney failure. Pathogenesis, interactions, and therapy].Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2015 Sep;110(6):452-8. doi: 10.1007/s00063-014-0404-x. Epub 2015 Feb 14. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2015. PMID: 25676118 Review. German.
-
Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: the multinational AKI-EPI study.Intensive Care Med. 2015 Aug;41(8):1411-23. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-3934-7. Epub 2015 Jul 11. Intensive Care Med. 2015. PMID: 26162677
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

