α7-cholinergic receptor mediates vagal induction of splenic norepinephrine
- PMID: 21339364
- PMCID: PMC3083451
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003722
α7-cholinergic receptor mediates vagal induction of splenic norepinephrine
Abstract
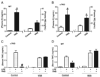
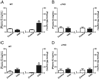
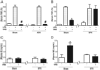
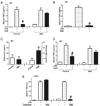
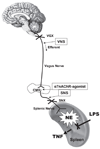
Classically, sympathetic and parasympathetic systems act in opposition to maintain the physiological homeostasis. In this article, we report that both systems work together to restrain systemic inflammation in life-threatening conditions such as sepsis. This study indicates that vagus nerve and cholinergic agonists activate the sympathetic noradrenergic splenic nerve to control systemic inflammation. Unlike adrenalectomy, splenectomy and splenic neurectomy prevent the anti-inflammatory potential of both the vagus nerve and cholinergic agonists, and abrogate their potential to induce splenic and plasma norepinephrine. Splenic nerve stimulation mimics vagal and cholinergic induction of norepinephrine and re-establishes neuromodulation in α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR)-deficient animals. Thus, vagus nerve and cholinergic agonists inhibit systemic inflammation by activating the noradrenergic splenic nerve via the α7nAChR nicotinic receptors. α7nAChR represents a unique molecular link between the parasympathetic and sympathetic system to control inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A distinct vagal anti-inflammatory pathway modulates intestinal muscularis resident macrophages independent of the spleen.Gut. 2014 Jun;63(6):938-48. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-304676. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Gut. 2014. PMID: 23929694
-
Apical splenic nerve electrical stimulation discloses an anti-inflammatory pathway relying on adrenergic and nicotinic receptors in myeloid cells.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Aug;80:238-246. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.03.015. Epub 2019 Mar 15. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 30885844
-
Central cholinergic activation of a vagus nerve-to-spleen circuit alleviates experimental colitis.Mucosal Immunol. 2014 Mar;7(2):335-47. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.52. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Mucosal Immunol. 2014. PMID: 23881354 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory properties of the vagus nerve: potential therapeutic implications of vagus nerve stimulation.J Physiol. 2016 Oct 15;594(20):5781-5790. doi: 10.1113/JP271539. Epub 2016 May 1. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27059884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholinergic modulation of the immune system presents new approaches for treating inflammation.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Nov;179:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 18. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28529069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture ameliorates intestinal inflammation by activating α7nAChR-mediated JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in postoperative ileus.Theranostics. 2021 Feb 19;11(9):4078-4089. doi: 10.7150/thno.52574. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33754049 Free PMC article.
-
Mediation of Cardiac Macrophage Activity via Auricular Vagal Nerve Stimulation Ameliorates Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Front Neurosci. 2020 Sep 8;14:906. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00906. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33013299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine mediates vagal modulation of the immune system by electroacupuncture.Nat Med. 2014 Mar;20(3):291-5. doi: 10.1038/nm.3479. Epub 2014 Feb 23. Nat Med. 2014. PMID: 24562381 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Acetylcholine System in Common Respiratory Diseases and COVID-19.Molecules. 2023 Jan 23;28(3):1139. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031139. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopaminergic Control of Inflammation and Glycemia in Sepsis and Diabetes.Front Immunol. 2018 May 4;9:943. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00943. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29780390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nathan C. Points of control in inflammation. Nature. 2002;420:846–852. - PubMed
-
- Ulloa L, Tracey KJ. The “cytokine profile”: a code for sepsis. Trends Mol. Med. 2005;11:56–63. - PubMed
-
- Tracey KJ, Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor: a pleiotropic cytokine and therapeutic target. Annu. Rev. Med. 1994;45:491–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

