Protein kinase LegK2 is a type IV secretion system effector involved in endoplasmic reticulum recruitment and intracellular replication of Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 21321072
- PMCID: PMC3088141
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00805-10
Protein kinase LegK2 is a type IV secretion system effector involved in endoplasmic reticulum recruitment and intracellular replication of Legionella pneumophila
Erratum in
-
Correction for Hervet et al., protein kinase LegK2 is a type IV secretion system effector involved in endoplasmic reticulum recruitment and intracellular replication of Legionella pneumophila.Infect Immun. 2015 Aug;83(8):3338. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00587-15. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26157087 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
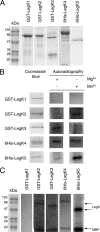
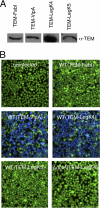
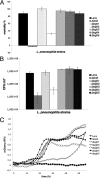
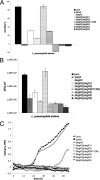
Legionella pneumophila is the etiological agent of Legionnaires' disease. Crucial to the pathogenesis of this intracellular pathogen is its ability to subvert host cell defenses, permitting intracellular replication in specialized vacuoles within host cells. The Dot/Icm type IV secretion system (T4SS), which translocates a large number of bacterial effectors into host cell, is absolutely required for rerouting the Legionella phagosome. Many Legionella effectors display distinctive eukaryotic domains, among which are protein kinase domains. In silico analysis and in vitro phosphorylation assays identified five functional protein kinases, LegK1 to LegK5, encoded by the epidemic L. pneumophila Lens strain. Except for LegK5, the Legionella protein kinases are all T4SS effectors. LegK2 plays a key role in bacterial virulence, as demonstrated by gene inactivation. The legK2 mutant containing vacuoles displays less-efficient recruitment of endoplasmic reticulum markers, which results in delayed intracellular replication. Considering that a kinase-dead substitution mutant of legK2 exhibits the same virulence defects, we highlight here a new molecular mechanism, namely, protein phosphorylation, developed by L. pneumophila to establish a replicative niche and evade host cell defenses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Legionella Kinase LegK2 Targets the ARP2/3 Complex To Inhibit Actin Nucleation on Phagosomes and Allow Bacterial Evasion of the Late Endocytic Pathway.mBio. 2015 May 5;6(3):e00354-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00354-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25944859 Free PMC article.
-
Viewing Legionella pneumophila Pathogenesis through an Immunological Lens.J Mol Biol. 2019 Oct 4;431(21):4321-4344. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.07.028. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31351897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Legionella pneumophila strain 130b possesses a unique combination of type IV secretion systems and novel Dot/Icm secretion system effector proteins.J Bacteriol. 2010 Nov;192(22):6001-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00778-10. Epub 2010 Sep 10. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20833813 Free PMC article.
-
An Indispensable Role for the MavE Effector of Legionella pneumophila in Lysosomal Evasion.mBio. 2021 Feb 9;12(1):e03458-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03458-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33563829 Free PMC article.
-
[Intracellular survival and replication of legionella pneumophila within host cells].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008 Dec;128(12):1763-70. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.128.1763. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 19043295 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Legionella Kinase LegK2 Targets the ARP2/3 Complex To Inhibit Actin Nucleation on Phagosomes and Allow Bacterial Evasion of the Late Endocytic Pathway.mBio. 2015 May 5;6(3):e00354-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00354-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25944859 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella pneumophila cell surface RtxA release by LapD/LapG and its role in virulence.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jul 19;24(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03395-1. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39026145 Free PMC article.
-
The Legionella Effector Kinase LegK7 Hijacks the Host Hippo Pathway to Promote Infection.Cell Host Microbe. 2018 Sep 12;24(3):429-438.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.08.004. Cell Host Microbe. 2018. PMID: 30212651 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylating Effectors of Legionella pneumophila: Finding the Sweet Spots for Host Cell Subversion.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 4;12(2):255. doi: 10.3390/biom12020255. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subversion of Cell-Autonomous Immunity and Cell Migration by Legionella pneumophila Effectors.Front Immunol. 2015 Sep 14;6:447. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00447. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26441958 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barz C., Abahji T. N., Trulzsch K., Heesemann J. 2000. The Yersinia Ser/Thr protein kinase YpkA/YopO directly interacts with the small GTPases RhoA and Rac-1. FEBS Lett. 482:139–143 - PubMed
-
- Berger K., Isberg R. 1993. Two distinct defects in intracellular growth complemented by a single genetic locus in Legionella pneumophila. Mol. Microbiol. 7:7–19 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

