MicroRNA-29c is a signature microRNA under high glucose conditions that targets Sprouty homolog 1, and its in vivo knockdown prevents progression of diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 21310958
- PMCID: PMC3064234
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.194969
MicroRNA-29c is a signature microRNA under high glucose conditions that targets Sprouty homolog 1, and its in vivo knockdown prevents progression of diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
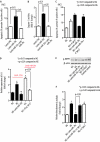
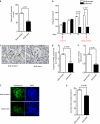
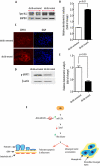
Although several recent publications have suggested that microRNAs contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy, the role of miRNAs in vivo still remains poorly understood. Using an integrated in vitro and in vivo comparative miRNA expression array, we identified miR-29c as a signature miRNA in the diabetic environment. We validated our profiling array data by examining miR-29c expression in the kidney glomeruli obtained from db/db mice in vivo and in kidney microvascular endothelial cells and podocytes treated with high glucose in vitro. Functionally, we found that miR-29c induces cell apoptosis and increases extracellular matrix protein accumulation. Indeed, forced expression of miR-29c strongly induced podocyte apoptosis. Conversely, knockdown of miR-29c prevented high glucose-induced cell apoptosis. We also identified Sprouty homolog 1 (Spry1) as a direct target of miR-29c with a nearly perfect complementarity between miR-29c and the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of mouse Spry1. Expression of miR-29c decreased the luciferase activity of Spry1 when co-transfected with the mouse Spry1 3'-UTR reporter construct. Overexpression of miR-29c decreased the levels of Spry1 protein and promoted activation of Rho kinase. Importantly, knockdown of miR-29c by a specific antisense oligonucleotide significantly reduced albuminuria and kidney mesangial matrix accumulation in the db/db mice model in vivo. These findings identify miR-29c as a novel target in diabetic nephropathy and provide new insights into the role of miR-29c in a previously unrecognized signaling cascade involving Spry1 and Rho kinase activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of miR-34c inhibits high glucose-induced apoptosis in podocytes by targeting Notch signaling pathways.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):4525-34. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191142 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-218 promotes high glucose-induced apoptosis in podocytes by targeting heme oxygenase-1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Mar 18;471(4):582-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.02.028. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26876575
-
MicroRNA-26a inhibits TGF-β-induced extracellular matrix protein expression in podocytes by targeting CTGF and is downregulated in diabetic nephropathy.Diabetologia. 2015 Sep;58(9):2169-80. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3642-4. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 26063197
-
Glomerular mesangial cell and podocyte injuries in diabetic nephropathy.Nephrology (Carlton). 2018 Oct;23 Suppl 4:32-37. doi: 10.1111/nep.13451. Nephrology (Carlton). 2018. PMID: 30298646 Review.
-
Study of microRNA in diabetic nephropathy: isolation, quantification and biological function.Nephrology (Carlton). 2015 Mar;20(3):132-9. doi: 10.1111/nep.12374. Nephrology (Carlton). 2015. PMID: 25487691 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibiting microRNA-192 ameliorates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Mar;23(3):458-69. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011050485. Epub 2012 Jan 5. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22223877 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-29b inhibits diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice.Mol Ther. 2014 Apr;22(4):842-53. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.235. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Mol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24445937 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNAs-genes regulatory network in diabetic nephropathy based on bioinformatics analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jul;98(27):e16225. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016225. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31277135 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-134-5p promotes high glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis by targeting bcl-2.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Mar 15;10(3):989-997. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29636888 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Diagnostic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles and Their miRNA Signature from Liquid Biopsy as Early Biomarkers of Diabetic Micro/Macrovascular Complications.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 14;18(9):1974. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091974. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28906481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambros V. (2004) Nature 431, 350–355 - PubMed
-
- Farh K. K., Grimson A., Jan C., Lewis B. P., Johnston W. K., Lim L. P., Burge C. B., Bartel D. P. (2005) Science 310, 1817–1821 - PubMed
-
- Croce C. M., Calin G. A. (2005) Cell 122, 6–7 - PubMed
-
- Urbich C., Kuehbacher A., Dimmeler S. (2008) Cardiovasc. Res. 79, 581–588 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

