Enhancers of adeno-associated virus AAV2 transduction via high throughput siRNA screening
- PMID: 21304495
- PMCID: PMC3129788
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2011.4
Enhancers of adeno-associated virus AAV2 transduction via high throughput siRNA screening
Abstract
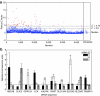
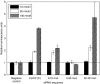
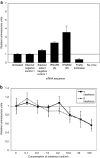
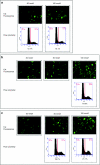
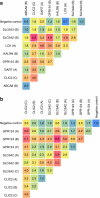
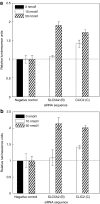
Intracellular barriers to adeno-associated virus (AAV) transduction may limit gene delivery. We screened a short interfering RNA (siRNA) library targeting 5,520 genes to help identify pathways that modulate AAV transduction of human endothelium. In replicate screening, 50 pools (three siRNAs per gene) resulted in greater than eightfold reporter gene expression enhancement. Single siRNA confirmation tests demonstrated that at least one siRNA from each of the top 10 pools provided greater than twofold enhancement. Several siRNAs when used together resulted in additive effects and two of the most potent siRNA sequences were enhancers in cultured airway epithelium. However, enhanced transduction was not correlated with mRNA knockdown by quantitative real time PCR, indicating an off-target mechanism. In fact, four of the five most potent siRNAs contained a consensus hexamer region 5'-UGUUUC-3' at positions 2-7 of the antisense strand. The point mutation U4A within this region (but not mutations at positions 1 or 14) disrupted transduction enhancement, indicating a microRNA (miRNA)-like mechanism. Transcription profiling indicated that the hexamer also resulted in perturbation of the interferon pathway via reduced interferon-induced protein 44-like (IFI44L), interferon-inducible myxovirus resistance 1 (MX1), and interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats (IFIT5) mRNAs. Direct interferon (α, β, and ω) receptor 2 (IFNAR2) knockdown resulted in greater than twofold transduction enhancement. In addition to providing insight into AAV biology and enhanced transduction, the results demonstrate certain beneficial siRNA off-target effects.
Figures
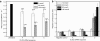
Similar articles
-
Suppression of transforming growth factor β1 in lung alveolar epithelium-derived cells using adeno-associated virus type 2/5 vectors to carry short hairpin RNA.Exp Lung Res. 2011 Apr;37(3):175-85. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2010.529985. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Exp Lung Res. 2011. PMID: 21269064
-
An siRNA Screen Identifies the U2 snRNP Spliceosome as a Host Restriction Factor for Recombinant Adeno-associated Viruses.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Aug 5;11(8):e1005082. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005082. eCollection 2015 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26244496 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative RNA profiling of TBEV-infected neurons and astrocytes reveals potential pathogenic effectors.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 May 30;20:2759-2777. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.05.052. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35685361 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide RNAi screening identifies host restriction factors critical for in vivo AAV transduction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 8;112(36):11276-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503607112. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26305933 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of putative miRNA binding sites and mRNA 3' ends as targets for siRNA-mediated gene knockdown.Oligonucleotides. 2009 Mar;19(1):41-52. doi: 10.1089/oli.2008.0154. Oligonucleotides. 2009. PMID: 19196098
Cited by
-
Host determinants of adeno-associated viral vector entry.Curr Opin Virol. 2017 Jun;24:124-131. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Curr Opin Virol. 2017. PMID: 28672171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular transport of recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors.Gene Ther. 2012 Jun;19(6):649-58. doi: 10.1038/gt.2012.6. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22357511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular trafficking of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors: challenges and future directions.Gene Ther. 2021 Dec;28(12):683-696. doi: 10.1038/s41434-021-00243-z. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Gene Ther. 2021. PMID: 33658649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicted deleterious variants in the human genome relevant to gene therapy with adeno-associated virus vectors.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023 Oct 13;31:101136. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2023.101136. eCollection 2023 Dec 14. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023. PMID: 38089635 Free PMC article.
-
Casein kinase 2 activity is a host restriction factor for AAV transduction.Mol Ther. 2024 Jan 3;32(1):84-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.11.010. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 37952087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartlett JS, Samulski RJ., and, McCown TJ. Selective and rapid uptake of adeno-associated virus type 2 in brain. Hum Gene Ther. 1998;9:1181–1186. - PubMed
-
- Chao H, Liu Y, Rabinowitz J, Li C, Samulski RJ., and, Walsh CE. Several log increase in therapeutic transgene delivery by distinct adeno-associated viral serotype vectors. Mol Ther. 2000;2:619–623. - PubMed
-
- Flotte TR, Zeitlin PL, Reynolds TC, Heald AE, Pedersen P, Beck S.et al. (2003Phase I trial of intranasal and endobronchial administration of a recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 2 (rAAV2)-CFTR vector in adult cystic fibrosis patients: a two-part clinical study Hum Gene Ther 141079–1088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

