MicroRNA signatures in tissues and plasma predict development and prognosis of computed tomography detected lung cancer
- PMID: 21300873
- PMCID: PMC3048155
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1100048108
MicroRNA signatures in tissues and plasma predict development and prognosis of computed tomography detected lung cancer
Abstract
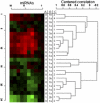
The efficacy of computed tomography (CT) screening for early lung cancer detection in heavy smokers is currently being tested by a number of randomized trials. Critical issues remain the frequency of unnecessary treatments and impact on mortality, indicating the need for biomarkers of aggressive disease. We explored microRNA (miRNA) expression profiles of lung tumors, normal lung tissues and plasma samples from cases with variable prognosis identified in a completed spiral-CT screening trial with extensive follow-up. miRNA expression patterns significantly distinguished: (i) tumors from normal lung tissues, (ii) tumor histology and growth rate, (iii) clinical outcome, and (iv) year of lung cancer CT detection. Interestingly, miRNA profiles in normal lung tissues also displayed remarkable associations with clinical features, suggesting the influence of a permissive microenvironment for tumor development. miRNA expression analyses in plasma samples collected 1-2 y before the onset of disease, at the time of CT detection and in disease-free smokers enrolled in the screening trial, resulted in the generation of miRNA signatures with strong predictive, diagnostic, and prognostic potential (area under the ROC curve ≥ 0.85). These signatures were validated in an independent cohort from a second randomized spiral-CT trial. These results indicate a role for miRNAs in lung tissues and plasma as molecular predictors of lung cancer development and aggressiveness and have theoretical and clinical implication for lung cancer management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical utility of a plasma-based miRNA signature classifier within computed tomography lung cancer screening: a correlative MILD trial study.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Mar 10;32(8):768-73. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.50.4357. Epub 2014 Jan 13. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24419137 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNA signature as liquid-biopsy to monitor lung cancer in low-dose computed tomography screening.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 20;6(32):32868-77. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5210. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26451608 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical evaluation of microRNA expression profiling in non small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2013 Sep;81(3):388-396. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Lung Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23756108
-
Circulating microRNA-422a is associated with lymphatic metastasis in lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(26):42173-42188. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15025. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28178679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-free microRNAs as diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers for lung cancer.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2013 Apr;52(4):356-69. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22032. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23404859 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in human solid tumors.Cancer Lett. 2013 Feb 28;329(2):125-36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.11.001. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23196059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as active players in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Oct 15;13(10):13227-39. doi: 10.3390/ijms131013227. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23202949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Level of Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000190 Correlates with Tumor Progression and Poor Treatment Response in Advanced Lung Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 30;12(7):1740. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071740. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32629833 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs: next-generation biomarkers for early lung cancer detection.Ecancermedicalscience. 2012;6:246. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2012.246. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Ecancermedicalscience. 2012. PMID: 22518197 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in using circulating miRNAs as cancer biomarkers.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:731479. doi: 10.1155/2015/731479. Epub 2015 Mar 22. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25874226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fontana RS, et al. Lung cancer screening: the Mayo program. J Occup Med. 1986;28:746–750. - PubMed
-
- Bach PB, et al. Computed tomography screening and lung cancer outcomes. JAMA. 2007;297:953–961. - PubMed
-
- Infante M, et al. DANTE Study Group. A randomized study of lung cancer screening with spiral computed tomography: three-year results from the DANTE trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:445–453. - PubMed
-
- Bach PB. Is our natural-history model of lung cancer wrong? Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:693–697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

