Wnt signaling regulates neuronal differentiation of cortical intermediate progenitors
- PMID: 21289176
- PMCID: PMC3040956
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5404-10.2011
Wnt signaling regulates neuronal differentiation of cortical intermediate progenitors
Abstract
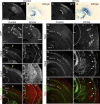
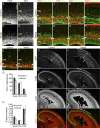
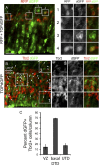
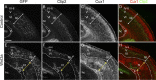
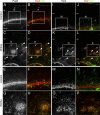
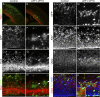
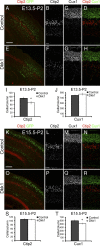
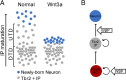
Cortical intermediate progenitors (IPs) comprise a secondary neuronal progenitor pool that arises from radial glia (RG). IPs are essential for generating the correct number of cortical neurons, but the factors that regulate the expansion and differentiation of IPs in the embryonic cortex are essentially unknown. In this study, we show that the Wnt-β-catenin pathway (canonical Wnt pathway) regulates IP differentiation into neurons. Upregulation of Wnt-β-catenin signaling by overexpression of Wnt3a in the neocortex induced early differentiation of IPs into neurons and the accumulation of these newly born neurons at the subventricular zone/intermediate zone border. Long-term overexpression of Wnt3a led to cortical dysplasia associated with the formation of large neuronal heterotopias. Conversely, downregulation of Wnt-β-catenin signaling with Dkk1 during mid and late stages of neurogenesis inhibited neuronal production. Consistent with previous reports, we show that Wnt-β-catenin signaling also promotes RG self-renewal. Thus, our findings show differential effects of the Wnt-β-catenin pathway on distinct groups of cortical neuronal progenitors: RG self-renewal and IP differentiation. Moreover, our findings suggest that dysregulation of Wnt signaling can lead to developmental defects similar to human cortical malformation disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pax6 mediates ß-catenin signaling for self-renewal and neurogenesis by neocortical radial glial stem cells.Stem Cells. 2014 Jan;32(1):45-58. doi: 10.1002/stem.1561. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 24115331 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic radial glia function as self-renewing neural progenitors in the absence of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Development. 2016 Jan 1;143(1):45-53. doi: 10.1242/dev.126813. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Development. 2016. PMID: 26603385 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulating Wnt signaling at different subcellular levels affects the fate of neonatal neural stem/progenitor cells.Brain Res. 2016 Nov 15;1651:73-87. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.09.026. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27659965
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway Governs a Full Program for Dopaminergic Neuron Survival, Neurorescue and Regeneration in the MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 24;19(12):3743. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123743. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30477246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Wnt Signaling in the Neurogenic Niche of the Adult Mouse Ventricular-Subventricular Zone.Neurochem Res. 2016 Feb;41(1-2):222-30. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1766-z. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 26572545 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA cluster miR-17-92 regulates neural stem cell expansion and transition to intermediate progenitors in the developing mouse neocortex.Cell Rep. 2013 May 30;3(5):1398-1406. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.037. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23623502 Free PMC article.
-
Growth and folding of the mammalian cerebral cortex: from molecules to malformations.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014 Apr;15(4):217-32. doi: 10.1038/nrn3707. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24646670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GDE2-Dependent Activation of Canonical Wnt Signaling in Neurons Regulates Oligodendrocyte Maturation.Cell Rep. 2020 May 5;31(5):107540. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107540. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32375055 Free PMC article.
-
GSK-3β Inhibition Induced Neuroprotection, Regeneration, and Functional Recovery After Intracerebral Hemorrhagic Stroke.Cell Transplant. 2017 Mar 13;26(3):395-407. doi: 10.3727/096368916X694364. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Cell Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28195036 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Role of Microtubule Stabilizing Agents in Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 26;18(8):1627. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081627. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28933765 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Backman M, Machon O, Mygland L, van den Bout CJ, Zhong W, Taketo MM, Krauss S. Effects of canonical Wnt signaling on dorso-ventral specification of the mouse telencephalon. Dev Biol. 2005;279:155–168. - PubMed
-
- Chenn A, Walsh CA. Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural precursors. Science. 2002;297:365–369. - PubMed
-
- Chenn A, Walsh CA. Increased neuronal production, enlarged forebrains and cytoarchitectural distortions in beta-catenin overexpressing transgenic mice. Cereb Cortex. 2003;13:599–606. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
