Pancreatic cancer cells respond to type I collagen by inducing snail expression to promote membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-dependent collagen invasion
- PMID: 21288898
- PMCID: PMC3060503
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.195628
Pancreatic cancer cells respond to type I collagen by inducing snail expression to promote membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-dependent collagen invasion
Abstract
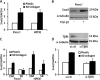
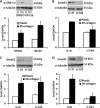
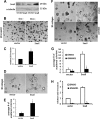
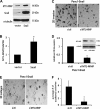
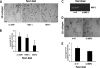
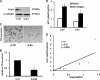
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is characterized by pronounced fibrotic reaction composed primarily of type I collagen. Although type I collagen functions as a barrier to invasion, pancreatic cancer cells have been shown to respond to type I collagen by becoming more motile and invasive. Because epithelial-mesenchymal transition is also associated with cancer invasion, we examined the extent to which collagen modulated the expression of Snail, a well known regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Relative to cells grown on tissue culture plastic, PDAC cells grown in three-dimensional collagen gels induced Snail. Inhibiting the activity or expression of the TGF-β type I receptor abrogated collagen-induced Snail. Downstream of the receptor, we showed that Smad3 and Smad4 were critical for the induction of Snail by collagen. In contrast, Smad2 or ERK1/2 was not involved in collagen-mediated Snail expression. Overexpression of Snail in PDAC cells resulted in a robust membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP, MMP-14)-dependent invasion through collagen-coated transwell chambers. Snail-expressing PDAC cells also demonstrated MT1-MMP-dependent scattering in three-dimensional collagen gels. Mechanistically, Snail increased the expression of MT1-MMP through activation of ERK-MAPK signaling, and inhibiting ERK signaling in Snail-expressing cells blocked two-dimensional collagen invasion and attenuated scattering in three-dimensional collagen. To provide in vivo support for our findings that Snail can regulate MT1-MMP, we examined the expression of Snail and MT1-MMP in human PDAC tumors and found a statistically significant positive correlation between MT1-MMP and Snail in these tumors. Overall, our data demonstrate that pancreatic cancer cells increase Snail on encountering collagen-rich milieu and suggest that the desmoplastic reaction actively contributes to PDAC progression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MT1-MMP cooperates with Kras(G12D) to promote pancreatic fibrosis through increased TGF-β signaling.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Oct;9(10):1294-304. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0023. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21856775 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen regulation of let-7 in pancreatic cancer involves TGF-β1-mediated membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase expression.Oncogene. 2011 Feb 24;30(8):1002-8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.485. Epub 2010 Nov 8. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21057545 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional collagen I promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer through MT1-MMP-mediated expression of HMGA2.Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 1;71(3):1019-28. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1855. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21148071 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between β1-integrin and Rho signaling regulates differential scattering and motility of pancreatic cancer cells by snail and Slug proteins.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6218-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.308940. Epub 2012 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22232555 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical role of the collagen-rich tumour microenvironment in pancreatic cancer progression.Biochem J. 2012 Jan 15;441(2):541-52. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111240. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22187935 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of Extracellular Matrix Rigidity Via Riboflavin-mediated Photocrosslinking Regulates Invasive Motility and Treatment Response in a 3D Pancreatic Tumor Model.Photochem Photobiol. 2020 Mar;96(2):365-372. doi: 10.1111/php.13191. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Photochem Photobiol. 2020. PMID: 31820435 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained elevation of Snail promotes glial-mesenchymal transition after irradiation in malignant glioma.Neuro Oncol. 2014 May;16(5):671-85. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not239. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Neuro Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24357458 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-directed coupling of endoglin and MMP-14 is a key mechanism for endoglin shedding and deregulation of TGF-β signaling.Oncogene. 2014 Jul 24;33(30):3970-9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.386. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24077288 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells to pancreatic cancer progression.J Surg Res. 2012 Mar;173(1):105-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2011.09.020. Epub 2011 Oct 8. J Surg Res. 2012. PMID: 22099597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Expression of Membrane Type 1-Matrix Metalloproteinase (Mt1-mmp/Mmp14) in the Mouse Embryo.Cells. 2021 Sep 17;10(9):2448. doi: 10.3390/cells10092448. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thiery J. P., Acloque H., Huang R. Y., Nieto M. A. (2009) Cell 139, 871–890 - PubMed
-
- Batlle E., Sancho E., Francí C., Domínguez D., Monfar M., Baulida J., García De Herreros A. (2000) Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 84–89 - PubMed
-
- Cano A., Pérez-Moreno M. A., Rodrigo I., Locascio A., Blanco M. J., del Barrio M. G., Portillo F., Nieto M. A. (2000) Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 76–83 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

