Anti-class a scavenger receptor autoantibodies from systemic lupus erythematosus patients impair phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells by macrophages in vitro
- PMID: 21281474
- PMCID: PMC3241353
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3230
Anti-class a scavenger receptor autoantibodies from systemic lupus erythematosus patients impair phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells by macrophages in vitro
Abstract
Introduction: Inadequate clearance of apoptotic cells by macrophages is one of the reasons for the breakdown of self-tolerance. Class A scavenger receptors, macrophage receptor with collagenous structure (MARCO) and scavenger receptor A (SR-A), which are expressed on macrophages, play important roles in the uptake of apoptotic cells. A previous study reported the presence of the anti-MARCO antibody in lupus-prone mice and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. The purpose of this study was to investigate the prevalence of anti-class A scavenger receptor antibodies in patients with various autoimmune diseases, in particular SLE, and the functional implication of those autoantibodies in the phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells by macrophages.
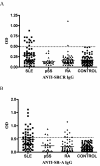
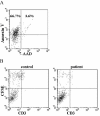
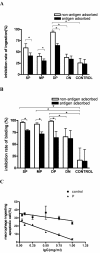
Methods: Purified recombinant scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) polypeptide (ligand-binding domain of MARCO) and recombinant SR-A were used as antigens. By using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, the anti-SRCR and anti-SR-A antibodies were detected in the sera of untreated patients with SLE (n = 65), rheumatoid arthritis (n = 65), primary Sjögren syndrome (n = 25), and healthy blood donors (n = 85). The effect of IgG purified from SLE patients or healthy controls on the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages was measured by the flow cytometry assay.
Results: Anti-SRCR antibodies were present in patients with SLE (18.5%) and rheumatoid arthritis (3.1%), but not in those with primary Sjögren syndrome. Anti-SR-A antibodies were present in patients with SLE (33.8%), rheumatoid arthritis (13.8%), and primary Sjögren syndrome (12.0%). IgG from SLE patients positive for anti-SRCR or anti-SR-A antibodies showed a higher inhibition rate on binding of apoptotic cells to macrophages than IgG from healthy controls (both P < 0.05). IgG from SLE patients positive for both anti-SRCR and anti-SR-A antibodies showed a significantly higher inhibition rate on ingestion of apoptotic by macrophages than IgG from healthy controls (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Our results indicated that autoantibodies to class A scavenger receptors might contribute to the breakdown of self-tolerance by impairing the clearance of apoptotic debris and play a role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease, especially in SLE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Tyro3 IgG Associates with Disease Activity and Reduces Efferocytosis of Macrophages in New-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.J Immunol Res. 2020 Nov 10;2020:2180708. doi: 10.1155/2020/2180708. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 33224991 Free PMC article.
-
Opsonization of late apoptotic cells by systemic lupus erythematosus autoantibodies inhibits their uptake via an Fcgamma receptor-dependent mechanism.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Oct;56(10):3399-411. doi: 10.1002/art.22947. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17907194
-
IgG autoantibodies against deposited C3 inhibit macrophage-mediated apoptotic cell engulfment in systemic autoimmunity.J Immunol. 2011 Sep 1;187(5):2101-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003468. Epub 2011 Aug 3. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21813769 Free PMC article.
-
SLE--a disease of clearance deficiency?Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 Sep;44(9):1101-7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh693. Epub 2005 May 31. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005. PMID: 15928001 Review.
-
Circulating microparticles in systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Dan Med J. 2012 Nov;59(11):B4548. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 23171755 Review.
Cited by
-
Cutting Edge: defective follicular exclusion of apoptotic antigens due to marginal zone macrophage defects in autoimmune BXD2 mice.J Immunol. 2013 May 1;190(9):4465-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300041. Epub 2013 Mar 29. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23543760 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage scavenger receptor 1 (Msr1, SR-A) influences B cell autoimmunity by regulating soluble autoantigen concentration.J Immunol. 2013 Aug 1;191(3):1055-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201680. Epub 2013 Jun 21. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23794629 Free PMC article.
-
The application of MARCO for immune regulation and treatment.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 1;51(1):246. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09201-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38300385 Review.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: Pathophysiological mechanisms related to innate immune system.SAGE Open Med. 2019 Sep 13;7:2050312119876146. doi: 10.1177/2050312119876146. eCollection 2019. SAGE Open Med. 2019. PMID: 35154753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microparticles bearing encephalitogenic peptides induce T-cell tolerance and ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Nat Biotechnol. 2012 Dec;30(12):1217-24. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2434. Epub 2012 Nov 18. Nat Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23159881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Emlen W, Niebur J, Kadera R. Accelerated in vitro apoptosis of lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1994;152:3685–3692. - PubMed
-
- Baumann I, Kolowos W, Voll RE, Manger B, Gaipl U, Neuhuber WL, Kirchner T, Kalden JR, Herrmann M. Impaired uptake of apoptotic cells into tingible body macrophages in germinal centers of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:191–201. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200201)46:1<191::AID-ART10027>3.0.CO;2-K. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herrmann M, Voll RE, Zoller OM, Hagenhofer M, Ponner BB, Kalden JR. Impaired phagocytosis of apoptotic cell material by monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:1241–1250. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199807)41:7<1241::AID-ART15>3.0.CO;2-H. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

