Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation
- PMID: 21279994
- PMCID: PMC3116142
- DOI: 10.1002/art.30115
Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation
Abstract
Objective: MicroRNA (miRNA) are recognized as important regulators of a variety of fundamental biologic processes. Previously, we described increased expression of miR-155 and miR-146a in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and showed a repressive effect of miR-155 on matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression in RA synovial fibroblasts (RASFs). The present study was undertaken to examine alterations in expression of miR-203 in RASFs and analyze its role in fibroblast activation.
Methods: Differentially expressed miRNA in RASFs versus osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts (OASFs) were identified by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based screening of 260 individual miRNA. Transfection of miR-203 precursor was used to analyze the function of miR-203 in RASFs. Levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and MMPs were measured by real-time PCR and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. RASFs were stimulated with IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and 5-azacytidine (5-azaC). Activity of IκB kinase 2 was inhibited with SC-514.
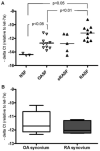
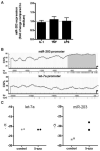
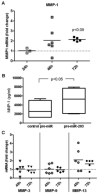
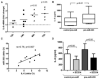
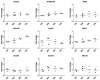
Results: Expression of miR-203 was higher in RASFs than in OASFs or fibroblasts from healthy donors. Levels of miR-203 did not change upon stimulation with IL-1β, TNFα, or LPS; however, DNA demethylation with 5-azaC increased the expression of miR-203. Enforced expression of miR-203 led to significantly increased levels of MMP-1 and IL-6. Induction of IL-6 by miR-203 overexpression was inhibited by blocking of the NF-κB pathway. Basal expression levels of IL-6 correlated with basal expression levels of miR-203.
Conclusion: The current results demonstrate methylation-dependent regulation of miR-203 expression in RASFs. Importantly, they also show that elevated levels of miR-203 lead to increased secretion of MMP-1 and IL-6 via the NF-κB pathway and thereby contribute to the activated phenotype of synovial fibroblasts in RA.
Copyright © 2011 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Altered expression of MicroRNA in synovial fibroblasts and synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Apr;58(4):1001-9. doi: 10.1002/art.23386. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18383392
-
Down-regulation of microRNA-34a* in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts promotes apoptosis resistance.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Jun;64(6):1771-9. doi: 10.1002/art.34334. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22161761
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 2: an important regulator of lnterleukin-6 production in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Oct;67(10):2624-33. doi: 10.1002/art.39256. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26139109
-
Epigenetic control in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009 May;5(5):266-72. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.55. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19412193 Review.
-
The role of non-coding RNAs (miRNA and lncRNA) in the clinical management of rheumatoid arthritis.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Dec;186:106549. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106549. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 36368452 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of molecular mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis using gene microarrays.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jun;13(6):4599-605. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5144. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27082252 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-21 Aggravates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in MH7A Cells Through Targeting SNF5.Inflammation. 2020 Apr;43(2):441-454. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01117-8. Inflammation. 2020. PMID: 32008163
-
Epigenetic alterations and microRNA misexpression in cancer and autoimmune diseases: a critical review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2014 Oct;47(2):128-35. doi: 10.1007/s12016-013-8401-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24362548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
-Omic Approaches and Treatment Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 8;14(8):1648. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081648. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012 Jan;18(1):187-93. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21691. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012. PMID: 21425211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–5. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–14. - PubMed
-
- Liu J. Control of protein synthesis and mRNA degradation by microRNAs. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:214–21. - PubMed
-
- Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Taganov KD. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:839–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

