The critical role of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4-mediated NF-κB activation in modified low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammatory gene expression and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 21278342
- PMCID: PMC3261755
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002242
The critical role of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4-mediated NF-κB activation in modified low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammatory gene expression and atherosclerosis
Abstract
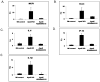
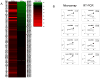
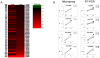
Exciting discoveries related to IL-1R/TLR signaling in the development of atherosclerosis plaque have triggered intense interest in the molecular mechanisms by which innate immune signaling modulates the onset and development of atherosclerosis. Previous studies have clearly shown the definitive role of proinflammatory cytokine IL-1 in the development of atherosclerosis. Recent studies have provided direct evidence supporting a link between innate immunity and atherogenesis. Although it is still controversial about whether infectious pathogens contribute to cardiovascular diseases, direct genetic evidence indicates the importance of IL-1R/TLR signaling in atherogenesis. In this study, we examined the role of IL-1R-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) kinase activity in modified low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-mediated signaling using bone marrow-derived macrophage as well as an in vivo model of atherosclerosis. First, we found that the IRAK4 kinase activity was required for modified LDL-induced NF-κB activation and expression of a subset of proinflammatory genes but not for the activation of MAPKs in bone marrow-derived macrophage. IRAK4 kinase-inactive knockin (IRAK4KI) mice were bred onto ApoE(-/-) mice to generate IRAK4KI/ApoE(-/-) mice. Importantly, the aortic sinus lesion formation was impaired in IRAK4KI/ApoE(-/-) mice compared with that in ApoE(-/-) mice. Furthermore, proinflammatory cytokine production was reduced in the aortic sinus region of IRAK4KI/ApoE(-/-) mice compared with that in ApoE(-/-) mice. Taken together, our results indicate that the IRAK4 kinase plays an important role in modified LDL-mediated signaling and the development of atherosclerosis, suggesting that pharmacological inhibition of IRAK4 kinase activity might be a feasible approach in the development of antiatherosclerosis drugs.
Figures
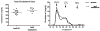



Similar articles
-
Pharmacological inhibition of IRAK1 and IRAK4 prevents endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Jan;175:106043. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.106043. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 34954030
-
New role of PCSK9 in atherosclerotic inflammation promotion involving the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Jul;262:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.04.023. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28535426
-
RIPK1 Expression Associates With Inflammation in Early Atherosclerosis in Humans and Can Be Therapeutically Silenced to Reduce NF-κB Activation and Atherogenesis in Mice.Circulation. 2021 Jan 12;143(2):163-177. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038379. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 33222501
-
Enzymatically modified LDL, atherosclerosis and beyond: paving the way to acceptance.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018 Jan 1;23(7):1257-1271. doi: 10.2741/4642. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018. PMID: 28930598 Review.
-
The immune system in atherosclerosis.Nat Immunol. 2011 Mar;12(3):204-12. doi: 10.1038/ni.2001. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21321594 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018 Aug;17(8):588-606. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.97. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 30026524 Review.
-
Proatherogenic conditions promote autoimmune T helper 17 cell responses in vivo.Immunity. 2014 Jan 16;40(1):153-65. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.021. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Immunity. 2014. PMID: 24412615 Free PMC article.
-
Relation between anti-atherosclerotic effects of IRAK4 and modulation of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype in diabetic rats.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Feb 15;8(2):899-910. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27158377 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of IRAK4 kinase activity improves ethanol-induced liver injury in mice.J Hepatol. 2020 Dec;73(6):1470-1481. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.016. Epub 2020 Jul 16. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32682051 Free PMC article.
-
Progranulin in the hematopoietic compartment protects mice from atherosclerosis.Atherosclerosis. 2018 Oct;277:145-154. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.08.042. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Atherosclerosis. 2018. PMID: 30212683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kirii H, Niwa T, Yamada Y, Wada H, Saito K, Iwakura Y, Asano M, Moriwaki H, Seishima M. Lack of interleukin-1beta decreases the severity of atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:656–660. - PubMed
-
- Chi H, Messas E, Levine RA, Graves DT, Amar S. Interleukin-1 receptor signaling mediates atherosclerosis associated with bacterial exposure and/or a high-fat diet in a murine apolipoprotein E heterozygote model: pharmacotherapeutic implications. Circulation. 2004;110:1678–1685. - PubMed
-
- Michelsen KS, Wong MH, Shah PK, Zhang W, Yano J, Doherty TM, Akira S, Rajavashisth TB, Arditi M. Lack of Toll-like receptor 4 or myeloid differentiation factor 88 reduces atherosclerosis and alters plaque phenotype in mice deficient in apolipoprotein E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:10679–10684. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

