Pol as a target for antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses in HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 21269655
- PMCID: PMC3056898
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.12.044
Pol as a target for antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses in HIV-1 infection
Abstract
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) may assist in preventing HIV or delaying disease progression. Most prior studies have analysed Env-specific ADCC responses. We hypothesized that effective ADCC-based immunity may target conserved internal viral proteins such as Pol. We analysed the ability overlapping Pol peptides to induce activation of NK cells via ADCC. We prospectively studied ADCC responses in 83 HIV+ subjects followed for 3 years. Pol peptides were commonly targeted by ADCC responses in these chronically infected subjects (in 32 of the 83 subjects). However, Pol-specific ADCC responses declined over time and did not correlate with delayed HIV progression, measured by either baseline CD4 T cells, CD4 T cell loss over time, baseline viral load or the need to start antiretroviral therapy. Although Pol is frequently targeted by ADCC in HIV+ subjects, the strength or specificity of Pol-specific ADCC responses needs to be modulated to be effective in delaying HIV progression.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

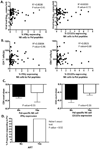
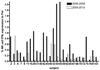
Similar articles
-
Specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses associated with slow progression of HIV infection.Immunology. 2013 Feb;138(2):116-23. doi: 10.1111/imm.12016. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23173935 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Combination Antiretroviral Therapy on HIV-1-specific Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Responses in Subtype B- and Subtype C-Infected Cohorts.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017 Jul 1;75(3):345-353. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001380. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017. PMID: 28346319 Clinical Trial.
-
The Early Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Response Is Associated With Lower Viral Set Point in Individuals With Primary HIV Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 9;9:2322. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02322. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30356637 Free PMC article.
-
Obstacles to ideal anti-HIV antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses.Vaccine. 2013 Nov 12;31(47):5506-17. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.08.035. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23981432 Review.
-
Unlocking HIV-1 Env: implications for antibody attack.AIDS Res Ther. 2017 Sep 12;14(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12981-017-0168-5. AIDS Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28893275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the potential of monoclonal antibody therapeutics for HIV-1 eradication.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2015 Jan;31(1):13-24. doi: 10.1089/aid.2014.0235. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2015. PMID: 25385703 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved HIV Epitopes for an Effective HIV Vaccine.J Clin Cell Immunol. 2017 Aug;8(4):518. doi: 10.4172/2155-9899.1000518. Epub 2017 Aug 30. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29226015 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NK cells by HIV-specific ADCC antibodies: role for granulocytes in expressing HIV-1 peptide epitopes.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 May;9(5):1011-8. doi: 10.4161/hv.23446. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23324623 Free PMC article.
-
Viral control in chronic HIV-1 subtype C infection is associated with enrichment of p24 IgG1 with Fc effector activity.AIDS. 2018 Jun 19;32(10):1207-1217. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001812. AIDS. 2018. PMID: 29620716 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Env- and Vpu-Specific Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Responses Associated with Elite Control of HIV.J Virol. 2017 Aug 24;91(18):e00700-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00700-17. Print 2017 Sep 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28701393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad A, Menezes J. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in HIV infections. Faseb J. 1996;10(2):258–266. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad R, Sindhu ST, Toma E, Morisset R, Vincelette J, Menezes J, Ahmad A. Evidence for a correlation between antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediating anti-HIV-1 antibodies and prognostic predictors of HIV infection. J Clin Immunol. 2001;21(3):227–233. - PubMed
-
- Alsmadi O, Tilley SA. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity directed against cells expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope of primary or laboratory-adapted strains by human and chimpanzee monoclonal antibodies of different epitope specificities. J Virol. 1998;72(1):286–293. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baum LL, Cassutt KJ, Knigge K, Khattri R, Margolick J, Rinaldo C, Kleeberger CA, Nishanian P, Henrard DR, Phair J. HIV-1 gp120-specific antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity correlates with rate of disease progression. J Immunol. 1996;157(5):2168–2173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

