Human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein induces KDM6A and KDM6B histone demethylase expression and causes epigenetic reprogramming
- PMID: 21245294
- PMCID: PMC3033314
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1009933108
Human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein induces KDM6A and KDM6B histone demethylase expression and causes epigenetic reprogramming
Abstract
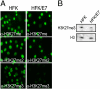
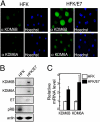
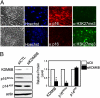
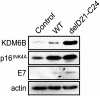
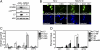
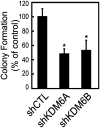
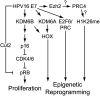
Despite the availability of vaccines, human papillomavirus (HPV) infections remain a cause of significant cancer morbidity and mortality. We have previously shown that HPV16 E7 associates with and diminishes E2F6-containing polycomb repressive complexes. Here, we show that repressive trimethyl marks on lysine 27 of histone 3, which are necessary for binding of polycomb repressive complexes, are decreased in HPV16 E7-expressing cells and HPV16-positive cervical lesions. This is caused by transcriptional induction of the KDM6A and KDM6B histone 3 lysine 27-specific demethylases. HPV16 E7-mediated KDM6B induction accounts for expression of the cervical cancer biomarker, p16(INK4A). Moreover, KDM6A- and KDM6B-responsive Homeobox genes are expressed at significantly higher levels, suggesting that HPV16 E7 results in reprogramming of host epithelial cells. These effects are independent of the ability of E7 to inhibit the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein. Most importantly, these effects are reversed when E7 expression is silenced, indicating that this pathway may have prognostic and/or therapeutic significance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
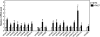
Similar articles
-
Tumor suppressor p16INK4A is necessary for survival of cervical carcinoma cell lines.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Oct 1;110(40):16175-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310432110. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24046371 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for alteration of EZH2, BMI1, and KDM6A and epigenetic reprogramming in human papillomavirus type 16 E6/E7-expressing keratinocytes.J Virol. 2011 Nov;85(21):10999-1006. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00160-11. Epub 2011 Aug 24. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21865393 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine Demethylase 6B Regulates Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation by Controlling c-MYC Expression.Mol Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;101(2):106-119. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.121.000372. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Mol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34862309
-
KDM6A-Mediated Expression of the Long Noncoding RNA DINO Causes TP53 Tumor Suppressor Stabilization in Human Papillomavirus 16 E7-Expressing Cells.J Virol. 2020 Jun 1;94(12):e02178-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02178-19. Print 2020 Jun 1. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32269126 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine Demethylase KDM6A in Differentiation, Development, and Cancer.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Sep 28;40(20):e00341-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00341-20. Print 2020 Sep 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32817139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An evaluation of p16(INK4a) expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia specimens, including women with HIV-1.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2012 Aug;107(5):571-7. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762012000500001. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2012. PMID: 22850945 Free PMC article.
-
The HPV16 oncogenes cause aberrant stem cell mobilization.Virology. 2013 Sep 1;443(2):218-25. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.04.008. Epub 2013 May 8. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23664148 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer associated human papillomaviruses.Curr Opin Virol. 2012 Aug;2(4):459-66. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jun 2. Curr Opin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22658985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p16INK4a immunocytochemistry versus human papillomavirus testing for triage of women with minor cytologic abnormalities: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cytopathol. 2012 Oct 25;120(5):294-307. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21205. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Cancer Cytopathol. 2012. PMID: 22700382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New P16 Expression Criteria Predict Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.In Vivo. 2019 Nov-Dec;33(6):1885-1892. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11682. In Vivo. 2019. PMID: 31662516 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

