Loqs-PD and R2D2 define independent pathways for RISC generation in Drosophila
- PMID: 21245036
- PMCID: PMC3089465
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1324
Loqs-PD and R2D2 define independent pathways for RISC generation in Drosophila
Abstract
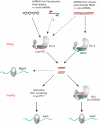
In Drosophila, siRNAs are classified as endo- or exo-siRNAs based on their origin. Both are processed from double-stranded RNA precursors by Dcr-2 and then loaded into the Argonaute protein Ago2. While exo-siRNAs serve to defend the cell against viruses, endo-siRNAs restrict the spread of selfish DNA in somatic cells, analogous to piRNAs in the germ line. Endo- and exo-siRNAs display a differential requirement for double-stranded RNA binding domain proteins (dsRBPs): R2D2 is needed to load exo-siRNAs into Ago2 while the PD isoform of Loquacious (Loqs-PD) stimulates Dcr-2 during the nucleolytic processing of hairpin-derived endo-siRNAs. In cell culture assays, R2D2 antagonizes Loqs-PD in endo-siRNA silencing and Loqs-PD is an inhibitor of RNA interference. Loqs-PD can interact via the C-terminus unique to this isoform with the DExH/D-helicase domain of Drosophila Dcr-2, where binding of R2D2 has also been localized. Separation of the two pathways is not complete; rather, the dicing and Ago2-loading steps appear uncoupled, analogous to the corresponding steps in miRNA biogenesis. Analysis of deep sequencing data further demonstrates that in r2d2 mutant flies, siRNAs can be loaded into Ago2 but not all siRNA classes are equally proficient for this. Thus, the canonical Ago2-RISC loading complex can be bypassed under certain circumstances.
© The Author(s) 2011. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
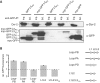

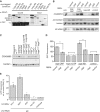
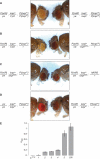
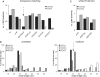
P{wIR}/yw; loqsko/CyO; P{loqs-PB}/+
P{wIR}/yw; loqsko/loqsf00791; +/+
P{wIR}/yw; loqsko/loqsf00791; P{loqs-PB}/+
P{wIR}/yw; loqsko/loqsko; P{loqs-PB}/+
yw/yw; loqsko/loqsko; P{loqs-PB}/+
Similar articles
-
R2D2 organizes small regulatory RNA pathways in Drosophila.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;31(4):884-96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01141-10. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21135122 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of R2D2, a cytoplasmic D2 body component, in the endogenous siRNA pathway in Drosophila.Mol Cell. 2013 Feb 21;49(4):680-91. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.12.024. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23375501
-
Molecular basis for asymmetry sensing of siRNAs by the Drosophila Loqs-PD/Dcr-2 complex in RNA interference.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Dec 1;45(21):12536-12550. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx886. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 29040648 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: Loquacious speaks out.Curr Biol. 2005 Aug 9;15(15):R603-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.044. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16085484 Review.
-
[Components and assembly of RNA-induced silencing complex].Yi Chuan. 2006 Jun;28(6):761-6. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 16818443 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Small-RNA asymmetry is directly driven by mammalian Argonautes.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;22(7):512-21. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3050. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26098316
-
Homology-dependent silencing by an exogenous sequence in the Drosophila germline.G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Mar;2(3):331-8. doi: 10.1534/g3.111.001925. Epub 2012 Mar 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 22413086 Free PMC article.
-
Dicer structure and function: conserved and evolving features.EMBO Rep. 2023 Jul 5;24(7):e57215. doi: 10.15252/embr.202357215. Epub 2023 Jun 13. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37310138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homology directed repair is unaffected by the absence of siRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 30;44(17):8261-71. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw570. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27353331 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic phosphate blocks binding of pre-miRNA to Dicer-2 via its PAZ domain.EMBO J. 2014 Feb 18;33(4):371-84. doi: 10.1002/embj.201387176. Epub 2014 Jan 31. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 24488111 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

