ATR-mediated phosphorylation of DNA polymerase η is needed for efficient recovery from UV damage
- PMID: 21242293
- PMCID: PMC3172178
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201008076
ATR-mediated phosphorylation of DNA polymerase η is needed for efficient recovery from UV damage
Abstract
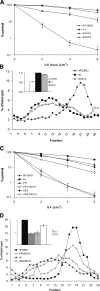
DNA polymerase η (polη) belongs to the Y-family of DNA polymerases and facilitates translesion synthesis past UV damage. We show that, after UV irradiation, polη becomes phosphorylated at Ser601 by the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated and Rad3-related (ATR) kinase. DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of polη depends on its physical interaction with Rad18 but is independent of PCNA monoubiquitination. It requires the ubiquitin-binding domain of polη but not its PCNA-interacting motif. ATR-dependent phosphorylation of polη is necessary to restore normal survival and postreplication repair after ultraviolet irradiation in xeroderma pigmentosum variant fibroblasts, and is involved in the checkpoint response to UV damage. Taken together, our results provide evidence for a link between DNA damage-induced checkpoint activation and translesion synthesis in mammalian cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of nucleotide excision repair factor xeroderma pigmentosum group A by ataxia telangiectasia mutated and Rad3-related-dependent checkpoint pathway promotes cell survival in response to UV irradiation.Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15;66(6):2997-3005. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3403. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16540648 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing effects of the UV lesion repair protein XPA and UV bypass polymerase eta on ATR checkpoint signaling.EMBO J. 2006 Jun 7;25(11):2605-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601123. Epub 2006 May 4. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16675950 Free PMC article.
-
ATR/Chk1 pathway is essential for resumption of DNA synthesis and cell survival in UV-irradiated XP variant cells.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 May 1;19(9):1690-701. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq046. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20123862
-
Checkpoint kinase ATR promotes nucleotide excision repair of UV-induced DNA damage via physical interaction with xeroderma pigmentosum group A.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24213-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.000745. Epub 2009 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19586908 Free PMC article.
-
Current state of knowledge of human DNA polymerase eta protein structure and disease-causing mutations.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2022 Jul-Dec;790:108436. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2022.108436. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2022. PMID: 35952573 Review.
Cited by
-
UBR5 interacts with the replication fork and protects DNA replication from DNA polymerase η toxicity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Dec 2;47(21):11268-11283. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz824. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31586398 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA damage checkpoint allows recombination between divergent DNA sequences in budding yeast.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 Nov 10;10(11):1086-94. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.07.007. Epub 2011 Oct 5. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21978436 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the abundance of Y-family polymerases in the cell cycle of budding yeast in response to DNA damage.Curr Genet. 2020 Aug;66(4):749-763. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01061-3. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32076806 Free PMC article.
-
The Functions of Serine 687 Phosphorylation of Human DNA Polymerase η in UV Damage Tolerance.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Jun;15(6):1913-20. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.052167. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26988343 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation regulates human polη stability and damage bypass throughout the cell cycle.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Sep 19;45(16):9441-9454. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx619. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28934491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya N., Yoon J.H., Gali H., Unk I., Haracska L., Johnson R.E., Hurwitz J., Prakash L., Prakash S. 2008. Roles of PCNA-binding and ubiquitin-binding domains in human DNA polymerase eta in translesion DNA synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 105:17724–17729 10.1073/pnas.0809844105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

