Wnt signaling during synaptic development and plasticity
- PMID: 21239163
- PMCID: PMC3499977
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2010.12.002
Wnt signaling during synaptic development and plasticity
Abstract
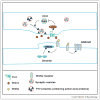
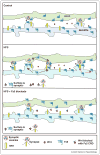
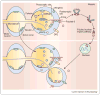
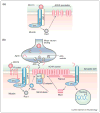
The formation of synaptic connections requires a dialogue between pre and postsynaptic cells to coordinate the assembly of the presynaptic release machinery and the postsynaptic receptive complexes. Signaling molecules of the Wnt family of proteins are central to this trans-synaptic dialogue. At the neuromuscular junction and central synapses, Wnts promote synaptic assembly by signaling to the developing pre and postsynaptic compartments. In addition, new studies reveal that expression of Wnt proteins and localization of their Fz receptors are regulated by neuronal activity. Importantly, Wnts mediates the synaptic changes induced by patterned neuronal activity or sensory experience in mature neurons. Here we review recent findings into the function of Wnt signaling at the synapse and its link to activity-dependent synaptic growth and function.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activity-mediated synapse formation a role for Wnt-Fz signaling.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011;97:119-36. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385975-4.00011-5. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 22074604
-
Postsynaptic assembly: a role for Wnt signaling.Dev Neurobiol. 2014 Aug;74(8):818-27. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22138. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Dev Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24105999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Canonical Wnt Signaling Modulates the Expression of Pre- and Postsynaptic Components in Different Temporal Patterns.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Mar;57(3):1389-1404. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01785-5. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31745835
-
Wnts: up-and-coming at the synapse.Trends Neurosci. 2007 Jun;30(6):268-75. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2007.04.003. Epub 2007 Apr 27. Trends Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17467065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Target-dependent retrograde signaling mediates synaptic plasticity at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.Dev Neurobiol. 2019 Nov;79(11-12):895-912. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22731. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Dev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31950660 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Wnt and lithium: a common destiny in the therapy of nervous system pathologies?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Apr;71(7):1123-48. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1378-1. Epub 2013 Jun 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 23749084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Catenin gain of function in muscles impairs neuromuscular junction formation.Development. 2012 Jul;139(13):2392-404. doi: 10.1242/dev.080705. Epub 2012 May 23. Development. 2012. PMID: 22627288 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling regulates experience-dependent synaptic plasticity in the adult nervous system.Cell Cycle. 2012 Jul 15;11(14):2585-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.21138. Epub 2012 Jul 15. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22781061 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways underlying the pathophysiology and treatment of depression: novel mechanisms for rapid-acting agents.Trends Neurosci. 2012 Jan;35(1):47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2011.11.004. Trends Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22217452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deficient Wnt Signaling and Synaptic Vulnerability in Alzheimer's Disease: Emerging Roles for the LRP6 Receptor.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2018 Oct 30;10:38. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2018.00038. eCollection 2018. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30425633 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Amerongen R, Nusse R. Towards an integrated view of Wnt signaling in development. Development. 2009;136:3205–3214. This is a comprehensive review on Wnt signaling that considers the integration of different cascades rather than the old view of distinct linear pathways. - PubMed
-
- Salinas PC. Retrograde signalling at the synapse: a role for Wnt proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33:1295–1298. - PubMed
-
- De Ferrari GV, Papassotiropoulos A, Biechele T, Wavrant De-Vrieze F, Avila ME, Major MB, Myers A, Saez K, Henriquez JP, Zhao A, et al. Common genetic variation within the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:9434–9439. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao C, Aviles C, Abel RA, Almli CR, McQuillen P, Pleasure SJ. Hippocampal and visuospatial learning defects in mice with a deletion of frizzled 9, a gene in the Williams syndrome deletion interval. Development. 2005;132:2917–2927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

