An upstream ORF with non-AUG start codon is translated in vivo but dispensable for translational control of GCN4 mRNA
- PMID: 21227927
- PMCID: PMC3082883
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1251
An upstream ORF with non-AUG start codon is translated in vivo but dispensable for translational control of GCN4 mRNA
Abstract
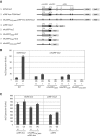
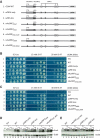
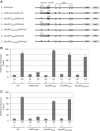
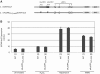
Genome-wide analysis of ribosome locations in mRNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae has revealed the translation of upstream open reading frames that initiate with near-cognate start codons in many transcripts. Two such non-translation initiation codon (AUG)-initiated upstream open reading frames (uORFs) (nAuORFs 1 and 2) occur in GCN4 mRNA upstream of the four AUG-initiated uORFs (uORFs 1-4) that regulate GCN4 translation. We verified that nAuORF2 is translated in vivo by demonstrating β-galactosidase production from lacZ coding sequences fused to nAuORF2, in a manner abolished by replacing its non-AUG initiation codon (AUA) start codon with the non-cognate triplet AAA, whereas translation of nAuORF1 was not detected. Importantly, replacing the near-cognate start codons of both nAuORFs with non-cognate triplets had little or no effect on the repression of GCN4 translation in non-starved cells, nor on its derepression in response to histidine limitation, nutritional shift-down or treatment with rapamycin, hydrogen peroxide or methyl methanesulfonate. Additionally, we found no evidence that initiation from the AUA codon of nAuORF2 is substantially elevated, or dependent on Gcn2, the sole eIF2α kinase of yeast, in histidine-deprived cells. Thus, although nAuORF2 is translated in vivo, it appears that this event is not stimulated by eIF2α phosphorylation nor significantly influences GCN4 translational induction under various starvation or stress conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
eIF1 discriminates against suboptimal initiation sites to prevent excessive uORF translation genome-wide.RNA. 2020 Apr;26(4):419-438. doi: 10.1261/rna.073536.119. Epub 2020 Jan 8. RNA. 2020. PMID: 31915290 Free PMC article.
-
Translation Initiation from Conserved Non-AUG Codons Provides Additional Layers of Regulation and Coding Capacity.mBio. 2017 Jun 27;8(3):e00844-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00844-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28655822 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between GCN2 and GCN4 expression, translation elongation factor 1 mutations and translational fidelity in yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Aug 12;33(14):4584-92. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki765. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16100380 Free PMC article.
-
Translational regulation by uORFs and start codon selection stringency.Genes Dev. 2023 Jun 1;37(11-12):474-489. doi: 10.1101/gad.350752.123. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 37433636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origin of translational control by eIF2α phosphorylation: insights from genome-wide translational profiling studies in fission yeast.Curr Genet. 2021 Jun;67(3):359-368. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01149-w. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33420908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism and Regulation of Protein Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2016 May;203(1):65-107. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186221. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27183566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temperature-dependent regulation of upstream open reading frame translation in S. cerevisiae.BMC Biol. 2019 Dec 6;17(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0718-5. BMC Biol. 2019. PMID: 31810458 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation analysis and the potential transcription regulator site in the extended KAP6.1 promoter in sheep.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Sep;41(9):6089-96. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3485-y. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24990691
-
Differential stability of Gcn4p controls its cell-specific activity in differentiated yeast colonies.mBio. 2024 May 8;15(5):e0068924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00689-24. Epub 2024 Apr 16. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38624209 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of scanning and start codon selection in eukaryotes.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Sep;75(3):434-67, first page of table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00008-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21885680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hinnebusch AG. Translational regulation of GCN4 and the general amino acid control of yeast. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2005;59:407–450. - PubMed
-
- Ron D, Harding HP. eIF2α phosphorylation in cellular stress responses and disease. In: Mathews M, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, editors. Translational Control in Biology and Medicine. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2007. pp. 345–368.
-
- Pestova TV, Lorsch JR, Hellen CUT. The mechanism of translation initiation in eukaryotes. In: Mathews M, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, editors. Translational Control in Biology and Medicine. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2007. pp. 87–128.
-
- Hinnebusch AG, Dever TE, Asano K. Mechanism of translation initiation in the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In: Mathews M, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, editors. Translational Control in Biology and Medicine. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2007. pp. 225–268.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

