Limitations in bonding to dentin and experimental strategies to prevent bond degradation
- PMID: 21220360
- PMCID: PMC3148178
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034510391799
Limitations in bonding to dentin and experimental strategies to prevent bond degradation
Abstract
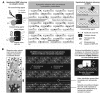
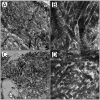
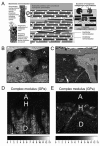
The limited durability of resin-dentin bonds severely compromises the lifetime of tooth-colored restorations. Bond degradation occurs via hydrolysis of suboptimally polymerized hydrophilic resin components and degradation of water-rich, resin-sparse collagen matrices by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and cysteine cathepsins. This review examined data generated over the past three years on five experimental strategies developed by different research groups for extending the longevity of resin-dentin bonds. They include: (1) increasing the degree of conversion and esterase resistance of hydrophilic adhesives; (2) the use of broad-spectrum inhibitors of collagenolytic enzymes, including novel inhibitor functional groups grafted to methacrylate resins monomers to produce anti-MMP adhesives; (3) the use of cross-linking agents for silencing the activities of MMP and cathepsins that irreversibly alter the 3-D structures of their catalytic/allosteric domains; (4) ethanol wet-bonding with hydrophobic resins to completely replace water from the extrafibrillar and intrafibrillar collagen compartments and immobilize the collagenolytic enzymes; and (5) biomimetic remineralization of the water-filled collagen matrix using analogs of matrix proteins to progressively replace water with intrafibrillar and extrafibrillar apatites to exclude exogenous collagenolytic enzymes and fossilize endogenous collagenolytic enzymes. A combination of several of these strategies should result in overcoming the critical barriers to progress currently encountered in dentin bonding.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ethanol wet-bonding challenges current anti-degradation strategy.J Dent Res. 2010 Dec;89(12):1499-504. doi: 10.1177/0022034510385240. Epub 2010 Oct 12. J Dent Res. 2010. PMID: 20940353 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of degradation of the hybrid layer in adhesive dentistry and therapeutic agents to improve bond durability--A literature review.Dent Mater. 2016 Feb;32(2):e41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2015.11.007. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Dent Mater. 2016. PMID: 26743967 Review.
-
Durability of resin-dentin bonds to water- vs. ethanol-saturated dentin.J Dent Res. 2009 Feb;88(2):146-51. doi: 10.1177/0022034508328910. J Dent Res. 2009. PMID: 19278986 Free PMC article.
-
Dentin adhesion and MMPs: a comprehensive review.J Esthet Restor Dent. 2013 Aug;25(4):219-41. doi: 10.1111/jerd.12016. Epub 2013 Feb 19. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2013. PMID: 23910180 Review.
-
[Applications of collagen extrafibrillar demineralization in dentin bonding].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Jan 9;58(1):81-85. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20220919-00494. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36642457 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Hydroxyapatite Affects the Physicochemical Properties of Contemporary One-Step Self-Etch Adhesives.Materials (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;15(22):8255. doi: 10.3390/ma15228255. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36431740 Free PMC article.
-
A quaternary ammonium silane antimicrobial triggers bacterial membrane and biofilm destruction.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 3;10(1):10970. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67616-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32620785 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering Interfacial Integrity with Hydrolytic-Resistant, Self-Reinforcing Dentin Adhesive.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 27;25(13):7061. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137061. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000170 Free PMC article.
-
Rechargeable dental adhesive with calcium phosphate nanoparticles for long-term ion release.J Dent. 2015 Dec;43(12):1587-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jul 2. J Dent. 2015. PMID: 26144190 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of MMP inhibitors incorporated within dental adhesives.J Dent Res. 2012 Jun;91(6):605-11. doi: 10.1177/0022034512446339. Epub 2012 Apr 18. J Dent Res. 2012. PMID: 22518030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aida M, Odaki M, Fujita K, Kitagawa T, Teshima I, Suzuki K, et al. (2009). Degradation-stage effect of self-etching primer on dentin bond durability. J Dent Res 88:443-448 - PubMed
-
- Amaral FL, Colucci V, Palma-Dibb RG, Corona SA. (2007). Assessment of in vitro methods used to promote adhesive interface degradation: a critical review. J Esthet Restor Dent 19:340-353 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong SR, Vargas MA, Chung I, Pashley DH, Campbell JA, Laffoon JE, et al. (2004). Resin-dentin interfacial ultrastructure and microtensile dentin bond strength after five-year water storage. Oper Dent 29:705-712 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

