Controlled enzymatic synthesis of natural-linkage, defined-length polyubiquitin chains using lysines with removable protecting groups
- PMID: 21212884
- PMCID: PMC3190230
- DOI: 10.1039/c0cc04868b
Controlled enzymatic synthesis of natural-linkage, defined-length polyubiquitin chains using lysines with removable protecting groups
Abstract
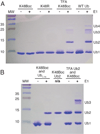
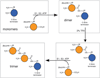
E2 enzymes catalyze the ATP-dependent polymerization of polyubiquitin chains which function as molecular signals in the regulation of numerous cellular processes. Here we present a method that uses genetically encoded unnatural amino acids to halt and re-start ubiquitin polymerization providing access to natural-linkage, precision-length ubiquitin chains that can be used for biochemical, structural, and dynamics studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enzymatic Assembly of Ubiquitin Chains.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1844:73-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8706-1_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30242704
-
Linkage-specific ubiquitin chain formation depends on a lysine hydrocarbon ruler.Nat Chem Biol. 2021 Mar;17(3):272-279. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-00696-0. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Nat Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33288957 Free PMC article.
-
Pivotal role for the ubiquitin Y59-E51 loop in lysine 48 polyubiquitination.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 10;111(23):8434-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1407849111. Epub 2014 May 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24912152 Free PMC article.
-
From seeds to trees: how E2 enzymes grow ubiquitin chains.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Feb 27;51(1):353-362. doi: 10.1042/BST20220880. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 36645006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The missing links to link ubiquitin: Methods for the enzymatic production of polyubiquitin chains.Anal Biochem. 2016 Jan 1;492:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2015.09.013. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Anal Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26470940 Review.
Cited by
-
Linkage via K27 Bestows Ubiquitin Chains with Unique Properties among Polyubiquitins.Structure. 2016 Mar 1;24(3):423-36. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Structure. 2016. PMID: 26876099 Free PMC article.
-
Reading and Writing the Ubiquitin Code Using Genetic Code Expansion.Chembiochem. 2024 Jun 3;25(11):e202400190. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202400190. Epub 2024 May 15. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 38588469 Review.
-
Modifying the vicinity of the isopeptide bond to reveal differential behavior of ubiquitin chains with interacting proteins: organic chemistry applied to synthetic proteins.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013 Oct 11;52(42):11149-53. doi: 10.1002/anie.201306118. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013. PMID: 24006204 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin Chains Bearing Genetically Encoded Photo-Cross-Linkers Enable Efficient Covalent Capture of (Poly)ubiquitin-Binding Domains.Biochemistry. 2019 Feb 19;58(7):883-886. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01089. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 30668904 Free PMC article.
-
Biocompatible Lysine Protecting Groups for the Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of K48/K63 Heterotypic and Branched Ubiquitin Chains.ACS Cent Sci. 2023 Jul 15;9(8):1633-1641. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.3c00389. eCollection 2023 Aug 23. ACS Cent Sci. 2023. PMID: 37637747 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

