Asf1/HIRA facilitate global histone deacetylation and associate with HP1 to promote nucleosome occupancy at heterochromatic loci
- PMID: 21211723
- PMCID: PMC3035992
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.12.009
Asf1/HIRA facilitate global histone deacetylation and associate with HP1 to promote nucleosome occupancy at heterochromatic loci
Abstract
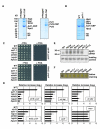
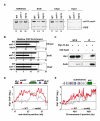
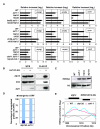
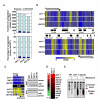
Heterochromatin impacts various nuclear processes by providing a recruiting platform for diverse chromosomal proteins. In fission yeast, HP1 proteins Chp2 and Swi6, which bind to methylated histone H3 lysine 9, associate with SHREC (Snf2/HDAC repressor complex) and Clr6 histone deacetylases (HDACs) involved in heterochromatic silencing. However, heterochromatic silencing machinery is not fully defined. We describe a histone chaperone complex containing Asf1 and HIRA that spreads across silenced domains via its association with Swi6 to enforce transcriptional silencing. Asf1 functions in concert with a Clr6 HDAC complex to silence heterochromatic repeats, and it suppresses antisense transcription by promoting histone deacetylation. Furthermore, we demonstrate that Asf1 and SHREC facilitate nucleosome occupancy at heterochromatic regions but TFIIIC transcription factor binding sites within boundary elements are refractory to these factors. These analyses uncover a role for Asf1 in global histone deacetylation and suggest that HP1-associated histone chaperone promotes nucleosome occupancy to assemble repressive heterochromatin.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
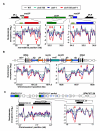
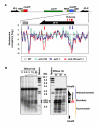

Comment in
-
New partners for HP1 in transcriptional gene silencing.Mol Cell. 2011 Jan 7;41(1):1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.12.021. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21211715 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Diverse roles of HP1 proteins in heterochromatin assembly and functions in fission yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jun 2;106(22):8998-9003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813063106. Epub 2009 May 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19443688 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Swi6/HP1-dependent heterochromatin assembly by cooperation of components of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and a histone deacetylase Clr6.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 8;279(41):42850-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407259200. Epub 2004 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15292231
-
HP1 proteins form distinct complexes and mediate heterochromatic gene silencing by nonoverlapping mechanisms.Mol Cell. 2008 Dec 26;32(6):778-90. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.10.026. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 19111658 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Chromatin States in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Jul 1;7(7):a018770. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018770. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 26134317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterochromatin revisited.Nat Rev Genet. 2007 Jan;8(1):35-46. doi: 10.1038/nrg2008. Nat Rev Genet. 2007. PMID: 17173056 Review.
Cited by
-
Centromeric heterochromatin assembly in fission yeast--balancing transcription, RNA interference and chromatin modification.Chromosome Res. 2012 Jul;20(5):521-34. doi: 10.1007/s10577-012-9288-x. Chromosome Res. 2012. PMID: 22733402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chd1 chromatin remodelers maintain nucleosome organization and repress cryptic transcription.EMBO Rep. 2012 Nov 6;13(11):997-1003. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.146. Epub 2012 Oct 2. EMBO Rep. 2012. PMID: 23032292 Free PMC article.
-
Shelterin and subtelomeric DNA sequences control nucleosome maintenance and genome stability.EMBO Rep. 2019 Jan;20(1):e47181. doi: 10.15252/embr.201847181. Epub 2018 Nov 12. EMBO Rep. 2019. PMID: 30420521 Free PMC article.
-
Cohesin Impedes Heterochromatin Assembly in Fission Yeast Cells Lacking Pds5.Genetics. 2019 Sep;213(1):127-141. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302256. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31278118 Free PMC article.
-
piRNA- and siRNA-mediated transcriptional repression in Drosophila, mice, and yeast: new insights and biodiversity.EMBO Rep. 2021 Oct 5;22(10):e53062. doi: 10.15252/embr.202153062. Epub 2021 Aug 4. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 34347367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adkins MW, Howar SR, Tyler JK. Chromatin disassembly mediated by the histone chaperone Asf1 is essential for transcriptional activation of the yeast PHO5 and PHO8 genes. Mol. Cell. 2004;14:657–666. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature. 2001;410:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Cam HP, Noma K, Ebina H, Levin HL, Grewal SIS. Host genome surveillance for retrotransposons by transposon-derived proteins. Nature. 2008;451:431–436. - PubMed
-
- Cam HP, Sugiyama T, Chen ES, Chen X, FitzGerald PC, Grewal SIS. Comprehensive analysis of heterochromatin- and RNAi-mediated epigenetic control of the fission yeast genome. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:809–819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

