Phosphodiesterase-4D knock-out and RNA interference-mediated knock-down enhance memory and increase hippocampal neurogenesis via increased cAMP signaling
- PMID: 21209202
- PMCID: PMC3079568
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5236-10.2011
Phosphodiesterase-4D knock-out and RNA interference-mediated knock-down enhance memory and increase hippocampal neurogenesis via increased cAMP signaling
Abstract
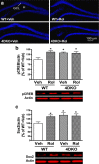
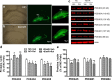
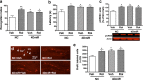
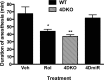
Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) plays an important role in mediating memory via the control of intracellular cAMP signaling; inhibition of PDE4 enhances memory. However, development of PDE4 inhibitors as memory enhancers has been hampered by their major side effect of emesis. PDE4 has four subtypes (PDE4A-D) consisting of 25 splice variants. Mice deficient in PDE4D displayed memory enhancement in radial arm maze, water maze, and object recognition tests. These effects were mimicked by repeated treatment with rolipram in wild-type mice. In addition, similarly as rolipram-treated wild-type mice, PDE4D-deficient mice also displayed increased hippocampal neurogenesis and phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein (pCREB). Furthermore, microinfusion of lentiviral vectors that contained microRNAs (miRNAs) targeting long-form PDE4D isoforms into bilateral dentate gyri of the mouse hippocampus downregulated PDE4D4 and PDE4D5, enhanced memory, and increased hippocampal neurogenesis and pCREB. Finally, while rolipram and PDE4D deficiency shortened α2 adrenergic receptor-mediated anesthesia, a surrogate measure of emesis, miRNA-mediated PDE4D knock-down in the hippocampus did not. The present results suggest that PDE4D, in particular long-form PDE4D, plays a critical role in the mediation of memory and hippocampal neurogenesis, which are mediated by cAMP/CREB signaling; reduced expression of PDE4D, or at least PDE4D4 and PDE4D5, in the hippocampus enhances memory but appears not to cause emesis. These novel findings will aid in the development of PDE4 subtype- or variant-selective inhibitors for treatment of disorders involving impaired cognition, including Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA interference-mediated knockdown of long-form phosphodiesterase-4D (PDE4D) enzyme reverses amyloid-β42-induced memory deficits in mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;38(2):269-80. doi: 10.3233/JAD-122236. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014. PMID: 23948935
-
RNA interference-mediated phosphodiesterase 4D splice variants knock-down in the prefrontal cortex produces antidepressant-like and cognition-enhancing effects.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;168(4):1001-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02225.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23003922 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase-4D Knock-down in the Prefrontal Cortex Alleviates Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depressive-Like Behaviors and Memory Deficits in Mice.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 10;5:11332. doi: 10.1038/srep11332. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26161529 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase-4 as a target for the development of antidepressant drugs.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(14):1688-98. doi: 10.2174/138161209788168092. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19442182 Review.
-
Research progress on phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors in central nervous system diseases.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jun 6;53(3):390-398. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2024-0023. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38860393 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese, English.
Cited by
-
Modeling cognitive dysfunction in neurofibromatosis-1.Trends Neurosci. 2013 Apr;36(4):237-47. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Trends Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23312374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dominant-Negative Attenuation of cAMP-Selective Phosphodiesterase PDE4D Action Affects Learning and Behavior.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 9;21(16):5704. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165704. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32784895 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding PDE4's function in Alzheimer's disease; a target for novel therapeutic approaches.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Oct 31;47(5):1557-1565. doi: 10.1042/BST20190763. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31642904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of PDE4 Inhibitor-Induced Hypothermia as a Correlate of Nausea in Mice.Biology (Basel). 2021 Dec 20;10(12):1355. doi: 10.3390/biology10121355. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943270 Free PMC article.
-
A negative allosteric modulator of PDE4D enhances learning after traumatic brain injury.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Feb;148:38-49. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.12.008. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 29294383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel T, Kandel E. Positive and negative regulatory mechanisms that mediate long-term memory storage. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998;26:360–378. - PubMed
-
- Barco A, Pittenger C, Kandel ER. CREB, memory enhancement and the treatment of memory disorders: promises, pitfalls and prospects. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003;7:101–114. - PubMed
-
- Bolger GB, McPhee I, Houslay MD. Alternative splicing of cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase mRNA transcripts: characterization of a novel tissue-specific isoform, RNPDE4A8. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:1065–1071. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
