Hsp90 and environmental stress transform the adaptive value of natural genetic variation
- PMID: 21205668
- PMCID: PMC3260023
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1195487
Hsp90 and environmental stress transform the adaptive value of natural genetic variation
Abstract
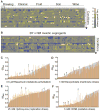
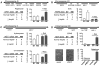
How can species remain unaltered for long periods yet also undergo rapid diversification? By linking genetic variation to phenotypic variation via environmental stress, the Hsp90 protein-folding reservoir might promote both stasis and change. However, the nature and adaptive value of Hsp90-contingent traits remain uncertain. In ecologically and genetically diverse yeasts, we find such traits to be both common and frequently adaptive. Most are based on preexisting variation, with causative polymorphisms occurring in coding and regulatory sequences alike. A common temperature stress alters phenotypes similarly. Both selective inhibition of Hsp90 and temperature stress increase correlations between genotype and phenotype. This system broadly determines the adaptive value of standing genetic variation and, in so doing, has influenced the evolution of current genomes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein folding sculpting evolutionary change.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2009;74:103-8. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2009.74.043. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2009. PMID: 20375316 Review.
-
It's not magic - Hsp90 and its effects on genetic and epigenetic variation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Apr;88:21-35. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.05.015. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 29807130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selection for robust metabolism in domesticated yeasts is driven by adaptation to Hsp90 stress.Science. 2024 Jul 26;385(6707):eadi3048. doi: 10.1126/science.adi3048. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Science. 2024. PMID: 39052788 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical biology: safeguards and spurs.Nature. 2003 Jul 31;424(6948):501-4. doi: 10.1038/424501a. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12891339 No abstract available.
-
Hsp90 depletion goes wild.BMC Biol. 2012 Feb 27;10:14. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-10-14. BMC Biol. 2012. PMID: 22369621 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hsp90 inhibitors and drug resistance in cancer: the potential benefits of combination therapies of Hsp90 inhibitors and other anti-cancer drugs.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Apr 15;83(8):995-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.11.011. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22120678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the Nature and Evolutionary Impact of Phenotypic Robustness Mechanisms.Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2014 Nov 1;45:496-517. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-120213-091705. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2014. PMID: 26034410 Free PMC article.
-
The Adaptive Potential of the Middle Domain of Yeast Hsp90.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Jan 23;38(2):368-379. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa211. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 32871012 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperativity of Negative Autoregulation Confers Increased Mutational Robustness.Phys Rev Lett. 2016 Jun 24;116(25):258104. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.258104. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Phys Rev Lett. 2016. PMID: 27391757 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal stress and mutation accumulation increase heat shock protein expression in Daphnia.Evol Ecol. 2022;36(5):829-844. doi: 10.1007/s10682-022-10209-1. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Evol Ecol. 2022. PMID: 36193163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindquist S, Craig EA. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631. - PubMed
-
- Neckers L. Heat shock protein 90: The cancer chaperone. J Biosci. 2007;32:517. - PubMed
-
- Jarosz DF, Taipale M, Lindquist S. Protein homeostasis and the phenotypic manifestation of genetic diversity: Principles and mechanisms. Annu Rev Genet. 2010;44:189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

