Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling plays an essential role in homeostasis of the intestine
- PMID: 21182089
- PMCID: PMC3250093
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201040479
Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling plays an essential role in homeostasis of the intestine
Abstract
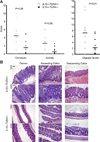
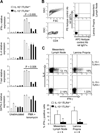
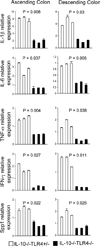
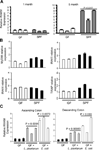
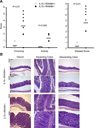
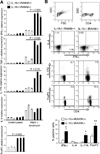
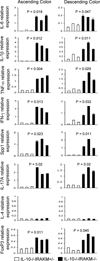
A healthy intestinal tract is characterized by controlled homeostasis due to the balanced interaction between commensal bacteria and the host mucosal immune system. Human and animal model studies have supported the hypothesis that breakdown of this homeostasis may underlie the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. However, it is not well understood how intestinal microflora stimulate the intestinal mucosal immune system and how such activation is regulated. Using a spontaneous, commensal bacteria-dependent colitis model in IL-10-deficient mice, we investigated the role of TLR and their negative regulation in intestinal homeostasis. In addition to IL-10(-/-) MyD88(-/-) mice, IL-10(-/-) TLR4(-/-) mice exhibited reduced colitis compared to IL-10(-/-) mice, indicating that TLR4 signaling plays an important role in inducing colitis. Interestingly, the expression of IRAK-M, a negative regulator of TLR signaling, is dependent on intestinal commensal flora, as IRAK-M expression was reduced in mice re-derived into a germ-free environment, and introduction of commensal bacteria into germ-free mice induced IRAK-M expression. IL-10(-/-) IRAK-M(-/-) mice exhibited exacerbated colitis with increased inflammatory cytokine gene expression. Therefore, this study indicates that intestinal microflora stimulate the colitogenic immune system through TLR and negative regulation of TLR signaling is essential in maintaining intestinal homeostasis.
Copyright © 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gnotobiotic IL-10-/-;NF-kappa B(EGFP) mice reveal the critical role of TLR/NF-kappa B signaling in commensal bacteria-induced colitis.J Immunol. 2007 May 15;178(10):6522-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.10.6522. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17475882
-
Toll-like receptor 2 dominance over Toll-like receptor 4 in stressful conditions for its detrimental role in the heart.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):H1238-H1247. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00800.2016. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28432060
-
Pathogenic and protective roles of MyD88 in leukocytes and epithelial cells in mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease.Gastroenterology. 2010 Aug;139(2):519-29, 529.e1-2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.045. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20433840 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor signaling and regulation of intestinal immunity.Virulence. 2013 Apr 1;4(3):207-12. doi: 10.4161/viru.23354. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Virulence. 2013. PMID: 23334153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental and natural infections in MyD88- and IRAK-4-deficient mice and humans.Eur J Immunol. 2012 Dec;42(12):3126-35. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242683. Eur J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23255009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome profiling reveals insight into distinct immune responses to Aeromonas salmonicida in gill of two rainbow trout strains.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2014 Jun;16(3):333-48. doi: 10.1007/s10126-013-9552-x. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2014. PMID: 24122123
-
IRAK-M expression limits dendritic cell activation and proinflammatory cytokine production in response to Helicobacter pylori.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 11;8(6):e66914. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066914. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776703 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor-agonist-based therapies for respiratory viral diseases: thinking outside the cell.Eur Respir Rev. 2022 May 4;31(164):210274. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0274-2021. Print 2022 Jun 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2022. PMID: 35508333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut.Nutrients. 2018 Feb 13;10(2):203. doi: 10.3390/nu10020203. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29438282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xuebijing exerts protective effects on lung permeability leakage and lung injury by upregulating Toll-interacting protein expression in rats with sepsis.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Dec;34(6):1492-504. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1943. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25269519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shiba T, Aiba Y, Ishikawa H, Ushiyama A, Takagi A, Mine T, Koga Y. The suppressive effect of bifidobacteria on Bacteroides vulgatus, a putative pathogenic microbe in inflammatory bowel disease. Microbiol Immunol. 2003;47:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Waidmann M, Bechtold O, Frick JS, Lehr HA, Schubert S, Dobrindt U, Loeffler J, Bohn E, Autenrieth IB. Bacteroides vulgatus protects against Escherichia coli-induced colitis in gnotobiotic interleukin-2-deficient mice. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:162–177. - PubMed
-
- Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science. 2005;307:1915–1920. - PubMed
-
- Macpherson AJ, Gatto D, Sainsbury E, Harriman GR, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel RM. A primitive T cell-independent mechanism of intestinal mucosal IgA responses to commensal bacteria. Science. 2000;288:2222–2226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

