The novel JAK inhibitor AZD1480 blocks STAT3 and FGFR3 signaling, resulting in suppression of human myeloma cell growth and survival
- PMID: 21164517
- PMCID: PMC3216671
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2010.289
The novel JAK inhibitor AZD1480 blocks STAT3 and FGFR3 signaling, resulting in suppression of human myeloma cell growth and survival
Abstract
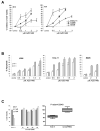
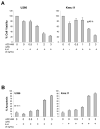
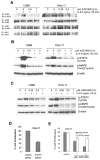
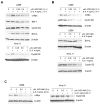
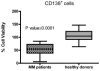
IL-6 and downstream JAK-dependent signaling pathways have critical roles in the pathophysiology of multiple myeloma (MM). We investigated the effects of a novel small-molecule JAK inhibitor (AZD1480) on IL-6/JAK signal transduction and its biological consequences on the human myeloma-derived cell lines U266 and Kms.11. At low micromolar concentrations, AZD1480 blocks cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of myeloma cell lines. These biological responses to AZD1480 are associated with concomitant inhibition of phosphorylation of JAK2, STAT3 and MAPK signaling proteins. In addition, there is inhibition of expression of STAT3 target genes, particularly Cyclin D2. Examination of a wider variety of myeloma cells (RPMI 8226, OPM-2, NCI-H929, Kms.18, MM1.S and IM-9), as well as primary myeloma cells, showed that AZD1480 has broad efficacy. In contrast, viability of normal peripheral blood (PB) mononuclear cells and CD138(+) cells derived from healthy controls was not significantly inhibited. Importantly, AZD1480 induces cell death of Kms.11 cells grown in the presence of HS-5 bone marrow (BM)-derived stromal cells and inhibits tumor growth in a Kms.11 xenograft mouse model, accompanied with inhibition of phospho-FGFR3, phospho-JAK2, phospho-STAT3 and Cyclin D2 levels. In sum, AZD1480 blocks proliferation, survival, FGFR3 and JAK/STAT3 signaling in myeloma cells cultured alone or cocultured with BM stromal cells, and in vivo. Thus, AZD1480 represents a potential new therapeutic agent for patients with MM.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of STAT3 with orally active JAK inhibitor, AZD1480, decreases tumor growth in Neuroblastoma and Pediatric Sarcomas In vitro and In vivo.Oncotarget. 2013 Mar;4(3):433-45. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.930. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 23531921 Free PMC article.
-
AZD1480, a JAK inhibitor, inhibits cell growth and survival of colorectal cancer via modulating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2014 Nov;32(5):1991-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3477. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25216185
-
Pharmacologic inhibition of Jak2-Stat5 signaling By Jak2 inhibitor AZD1480 potently suppresses growth of both primary and castrate-resistant prostate cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Oct 15;19(20):5658-74. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0422. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23942095 Free PMC article.
-
The role of JAK inhibitors in multiple myeloma.Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2019 Sep;17(9):500-505. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31549971 Review.
-
[Research Progress on Effect of Bone Marrow Microenvironment Regulated by IL-6/IL-6R/JAK2/STAT3 Pathway on Biological Behavior of Multiple Myeloma--Review].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Feb;32(1):318-321. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2024.01.052. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38387942 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of STAT3 with orally active JAK inhibitor, AZD1480, decreases tumor growth in Neuroblastoma and Pediatric Sarcomas In vitro and In vivo.Oncotarget. 2013 Mar;4(3):433-45. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.930. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 23531921 Free PMC article.
-
Kinase inhibitors as potential agents in the treatment of multiple myeloma.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):81926-81968. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10745. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27655636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting treatment resistance: unveiling the potential of RNA methylation regulators and TG-101,209 in pan-cancer neoadjuvant therapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 19;43(1):232. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03111-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39160604 Free PMC article.
-
The consequences of selective inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) tyrosine705 phosphorylation by phosphopeptide mimetic prodrugs targeting the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain.JAKSTAT. 2012 Oct 1;1(4):263-347. doi: 10.4161/jkst.22682. JAKSTAT. 2012. PMID: 24058783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chk1 Inhibition Potently Blocks STAT3 Tyrosine705 Phosphorylation, DNA-Binding Activity, and Activation of Downstream Targets in Human Multiple Myeloma Cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 1;20(3):456-467. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-21-0366. Mol Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 34782371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fonseca R, Stewart AK. Targeted therapeutics for multiple myeloma: the arrival of a risk-stratified approach. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):802–810. - PubMed
-
- San-Miguel J, Harousseau JL, Joshua D, Anderson KC. Individualizing treatment of patients with myeloma in the era of novel agents. J Clin Oncol. 2008 Jun 1;26(16):2761–2766. - PubMed
-
- Ocio EM, Mateos MV, Maiso P, Pandiella A, San-Miguel JF. New drugs in multiple myeloma: mechanisms of action and phase I/II clinical findings. Lancet Oncol. 2008 Dec;9(12):1157–1165. - PubMed
-
- Vallet S, Palumbo A, Raje N, Boccadoro M, Anderson KC. Thalidomide and lenalidomide: Mechanism-based potential drug combinations. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008 Jul;49(7):1238–1245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

