Innovative immunohistochemistry identifies MMP-9 expressing macrophages at the invasive front of murine HCC
- PMID: 21160992
- PMCID: PMC2999283
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i5.175
Innovative immunohistochemistry identifies MMP-9 expressing macrophages at the invasive front of murine HCC
Abstract
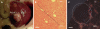
Aim: To investigate the proteolytic contribution of tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) in tumor invasion, we analyzed whether TAM at the invasive front of small HCC in Abcb4(-/-)-mice show an enhanced expression of MMP-9.
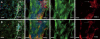
Methods: Liver cryosections of the hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) invasive front from 12 mo old Abcb4(-/-)-mice were stained for collagen type I and MMP-9 using Alexa488 and Alexa568 labeled secondary antibodies. Afterwards, the Alexa568 dye was bleached and the macrophage marker F4/80 was visualized using Alexa568 labeled secondary antibodies. Finally, photographs of the invasive tumor front were digitally overlaid and analyzed.
Results: After complete bleaching of the primary dye, specific fluorescence staining of a third antigen, here F4/80, was successfully performed on the same histological section. With this method, we were able to identify conglomerates of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-9) expressing macrophages within the tumor capsule of HCC.
Conclusion: MMP-9 expressing macrophages are involved in matrix remodelling at the invasive tumor front of HCC. The described staining protocol provides a simple yet powerful extension of conventional immuno-histochemistry, facilitating visualization of at least three different antigens plus nuclei in one single histological section.
Keywords: Fluorescence staining; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Matrix metalloproteinase; Tumor associated macrophages.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of MMP-2, -9 and TIMP-1,-2 immunoreactive protein at the invasive front in advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Pathol Res Pract. 2002;198(8):509-15. doi: 10.1078/S0344-0338(04)70292-7. Pathol Res Pract. 2002. PMID: 12389993
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 expression and synthetic matrix metalloproteinase-2 inhibitor binding in ovarian carcinomas and tumor cell lines.Lab Invest. 1996 Feb;74(2):406-21. Lab Invest. 1996. PMID: 8780160
-
Fibulin-5 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by down-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression.BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 12;14:938. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-938. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25494879 Free PMC article.
-
Expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 and their effects on angiogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Oct 14;11(38):5931-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.5931. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16273602 Free PMC article.
-
Invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines: contribution of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase.Neoplasia. 1999 Nov;1(5):424-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900046. Neoplasia. 1999. PMID: 10933057 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cholestasis impairs hepatic lipid storage via AMPK and CREB signaling in hepatitis B virus surface protein transgenic mice.Lab Invest. 2020 Nov;100(11):1411-1424. doi: 10.1038/s41374-020-0457-9. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Lab Invest. 2020. PMID: 32612285 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrogenesis and Carcinogenesis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Involvement of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinase (TIMPs).Cancers (Basel). 2014 Jun 27;6(3):1220-55. doi: 10.3390/cancers6031220. Cancers (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24978432 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in gastrointestinal cancers: A systemic review.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Jan 15;13(1):1-11. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i1.1. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33510845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2015 Oct;62(4):1304-12. doi: 10.1002/hep.27867. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25914264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The inflammatory microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: a pivotal role for tumor-associated macrophages.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:187204. doi: 10.1155/2013/187204. Epub 2012 Dec 30. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23533994 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Katzenellenbogen M, Pappo O, Barash H, Klopstock N, Mizrahi L, Olam D, Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Rechavi G, Mitchell LA, et al. Multiple adaptive mechanisms to chronic liver disease revealed at early stages of liver carcinogenesis in the Mdr2-knockout mice. Cancer Res. 2006;66:4001–4010. - PubMed
-
- Smit JJ, Schinkel AH, Oude Elferink RP, Groen AK, Wagenaar E, van Deemter L, Mol CA, Ottenhoff R, van der Lugt NM, van Roon MA. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell. 1993;75:451–462. - PubMed
-
- Classon M, Settleman J. Emerging concepts in tumor progression and therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2000;10:393–397. - PubMed
-
- Egeblad M, Werb Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:161–174. - PubMed
-
- Zucker S, Vacirca J. Role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004;23:101–117. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

