Drosophila miR-14 regulates insulin production and metabolism through its target, sugarbabe
- PMID: 21159815
- PMCID: PMC3003191
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1995910
Drosophila miR-14 regulates insulin production and metabolism through its target, sugarbabe
Abstract
Energy homeostasis depends on insulin signaling in metazoans. Insulin levels reflect the nutritional status of the animal to control levels of circulating sugar and regulate storage of resources in the form of glycogen and fat. Over the past several years, evidence has begun to accumulate that insulin production and secretion, as well as cellular responsiveness to insulin, are subject to regulation by microRNAs. Here we present evidence that miR-14 acts in the insulin-producing neurosecretory cells in the adult Drosophila brain to control metabolism. miR-14 acts in these cells through its direct target, sugarbabe. sugarbabe encodes a predicted zinc finger protein that regulates insulin gene expression in the neurosecretory cells. Regulation of sugarbabe levels by nutrients and by miR-14 combines to allow the fly to manage resource mobilization in a nutritionally variable environment.
Figures
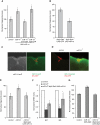
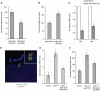
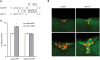
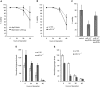
Similar articles
-
Drosophila lacking microRNA miR-278 are defective in energy homeostasis.Genes Dev. 2006 Feb 15;20(4):417-22. doi: 10.1101/gad.374406. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16481470 Free PMC article.
-
Mio acts in the Drosophila brain to control nutrient storage and feeding.Gene. 2015 Sep 1;568(2):190-5. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.05.055. Epub 2015 May 27. Gene. 2015. PMID: 26024590 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of insulin and Notch pathway activities by microRNA miR-305 mediates adaptive homeostasis in the intestinal stem cells of the Drosophila gut.Genes Dev. 2014 Nov 1;28(21):2421-31. doi: 10.1101/gad.241588.114. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 25367037 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin/TOR signaling in growth and homeostasis: a view from the fly world.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 May;41(5):1006-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.10.010. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18992839 Review.
-
Insulin/IGF signaling and its regulation in Drosophila.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2015 Sep 15;221:255-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.11.021. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25616197 Review.
Cited by
-
The Biological Roles of microRNAs in Drosophila Development.Insects. 2024 Jun 30;15(7):491. doi: 10.3390/insects15070491. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39057224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extensive circadian and light regulation of the transcriptome in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae.BMC Genomics. 2013 Apr 3;14:218. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-218. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23552056 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of miRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster Male Courtship Behavior.Genetics. 2019 Mar;211(3):925-942. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301901. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30683757 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of insect behavior by non-coding RNAs.Sci China Life Sci. 2024 Jun;67(6):1106-1118. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2482-2. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Sci China Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38443665 Review.
-
Death following traumatic brain injury in Drosophila is associated with intestinal barrier dysfunction.Elife. 2015 Mar 5;4:e04790. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04790. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25742603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Böhni R, Riesgo-Escovar J, Oldham S, Brogiolo W, Stocker H, Andruss BF, Beckingham K, Hafen E 1999. Autonomous control of cell and organ size by CHICO, a Drosophila homolog of vertebrate IRS1-4. Cell 97: 865–875 - PubMed
-
- Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM 2003. bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the pro-apoptotic gene hid in Drosophila . Cell 113: 25–36 - PubMed
-
- Brogiolo W, Stocker H, Ikeya T, Rintelen F, Fernandez R, Hafen E 2001. An evolutionarily conserved function of the Drosophila insulin receptor and insulin-like peptides in growth control. Curr Biol 11: 213–221 - PubMed
-
- Cao C, Brown MR 2001. Localization of an insulin-like peptide in brains of two flies. Cell Tissue Res 304: 317–321 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
