Three sorting nexins drive the degradation of apoptotic cells in response to PtdIns(3)P signaling
- PMID: 21148288
- PMCID: PMC3031466
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-09-0756
Three sorting nexins drive the degradation of apoptotic cells in response to PtdIns(3)P signaling
Abstract
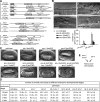
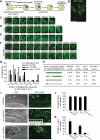
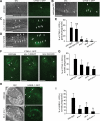
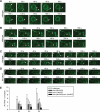
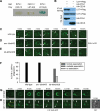
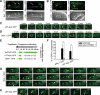
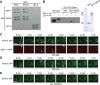
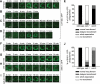
Apoptotic cells are swiftly engulfed by phagocytes and degraded inside phagosomes. Phagosome maturation requires phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PtdIns(3)P], yet how PtdIns(3)P triggers phagosome maturation remains largely unknown. Through a genomewide PtdIns(3)P effector screen in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans , we identified LST-4/SNX9, SNX-1, and SNX-6, three BAR domain-containing sorting nexins, that act in two parallel pathways to drive PtdIns(3)P-mediated degradation of apoptotic cells. We found that these proteins were enriched on phagosomal surfaces through association with PtdIns(3)P and through specific protein-protein interaction, and they promoted the fusion of early endosomes and lysosomes to phagosomes, events essential for phagosome maturation. Specifically, LST-4 interacts with DYN-1 (dynamin), an essential phagosome maturation initiator, to strengthen DYN-1's association to phagosomal surfaces, and facilitates the maintenance of the RAB-7 GTPase on phagosomal surfaces. Furthermore, both LST-4 and SNX-1 promote the extension of phagosomal tubules to facilitate the docking and fusion of intracellular vesicles. Our findings identify the critical and differential functions of two groups of sorting nexins in phagosome maturation and reveal a signaling cascade initiated by phagocytic receptor CED-1, mediated by PtdIns(3)P, and executed through these sorting nexins to degrade apoptotic cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Programmed cell death and clearance of cell corpses in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Jun;73(11-12):2221-36. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2196-z. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27048817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PtdIns(4,5)P₂ and PtdIns3P coordinate to regulate phagosomal sealing for apoptotic cell clearance.J Cell Biol. 2015 Aug 3;210(3):485-502. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201501038. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26240185 Free PMC article.
-
Phagocytic receptor CED-1 initiates a signaling pathway for degrading engulfed apoptotic cells.PLoS Biol. 2008 Mar 18;6(3):e61. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060061. PLoS Biol. 2008. PMID: 18351800 Free PMC article.
-
The small GTPase RAB-35 defines a third pathway that is required for the recognition and degradation of apoptotic cells.PLoS Genet. 2018 Aug 23;14(8):e1007558. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007558. eCollection 2018 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30138370 Free PMC article.
-
Phagosome maturation during the removal of apoptotic cells: receptors lead the way.Trends Cell Biol. 2008 Oct;18(10):474-85. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.08.002. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Trends Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18774293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Programmed cell death and clearance of cell corpses in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Jun;73(11-12):2221-36. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2196-z. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27048817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A conserved requirement for RME-8/DNAJC13 in neuronal autophagic lysosome reformation.Autophagy. 2024 Apr;20(4):792-808. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2269028. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 37942902 Free PMC article.
-
Response of G protein-coupled receptor CED-1 in germline to polystyrene nanoparticles in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 Feb 17;3(7):1997-2006. doi: 10.1039/d0na00867b. eCollection 2021 Apr 6. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 36133095 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed Cell Death During Caenorhabditis elegans Development.Genetics. 2016 Aug;203(4):1533-62. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186247. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27516615 Free PMC article.
-
Components of the Engulfment Machinery Have Distinct Roles in Corpse Processing.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 27;11(6):e0158217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158217. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27347682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Backer JM. The regulation and function of Class III PI3Ks: novel roles for Vps34. Biochem J. 2008;410:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Bai C, Elledge SJ. Gene identification using the yeast two-hybrid system. Methods Enzymol. 1997;283:141–156. - PubMed
-
- Birkeland HC, Stenmark H. Protein targeting to endosomes and phagosomes via FYVE and PX domains. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004;282:89–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

