Phospholipase d2 ablation ameliorates Alzheimer's disease-linked synaptic dysfunction and cognitive deficits
- PMID: 21147981
- PMCID: PMC3004537
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3317-10.2010
Phospholipase d2 ablation ameliorates Alzheimer's disease-linked synaptic dysfunction and cognitive deficits
Abstract
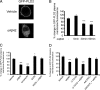
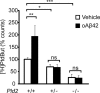
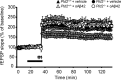
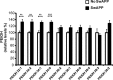
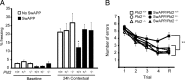
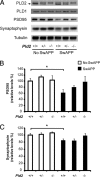
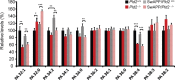
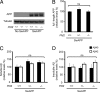
Growing evidence implicates aberrant lipid signaling in Alzheimer's disease (AD). While phospholipases A2 and C have been recently shown to mediate key actions of amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) through a dysregulation of arachidonic acid and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate metabolism, respectively, the role of phospholipase D (PLD) has so far remained elusive. PLD produces phosphatidic acid (PA), a bioactive lipid involved in multiple aspects of cell physiology, including signaling and membrane trafficking processes. Here we show that oligomeric Aβ enhances PLD activity in cultured neurons and that this stimulatory effect does not occur upon ablation of PLD2 via gene targeting. Aβ fails to suppress long-term potentiation in PLD2-deficient hippocampal slices, suggesting that PLD2 is required for the synaptotoxic action of this peptide. In vivo PLD activity, as assessed by detection of phosphatidylethanol levels using mass spectrometry (MS) following ethanol injection, is also increased in the brain of a transgenic mouse model of AD (SwAPP). Furthermore, Pld2 ablation rescues memory deficits and confers synaptic protection in SwAPP mice despite a significant Aβ load. MS-based lipid analysis of Pld2 mutant brains in the presence or absence of the SwAPP transgene unmasks striking crosstalks between different PA species. This lipid analysis shows an exquisite acyl chain specificity and plasticity in the perturbation of PA metabolism. Collectively, our results point to specific molecular species of PA as key modulators of AD pathogenesis and identify PLD2 as a novel potential target for therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Partial reduction of BACE1 improves synaptic plasticity, recent and remote memories in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice.J Neurochem. 2010 Apr;113(1):248-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06608.x. Epub 2010 Jan 20. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20089133 Free PMC article.
-
Ciliary neurotrophic factor cell-based delivery prevents synaptic impairment and improves memory in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci. 2010 Jun 2;30(22):7516-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4182-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20519526 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase A2 reduction ameliorates cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Nat Neurosci. 2008 Nov;11(11):1311-8. doi: 10.1038/nn.2213. Epub 2008 Oct 19. Nat Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18931664 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian phospholipase D: Function, and therapeutics.Prog Lipid Res. 2020 Apr;78:101018. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2019.101018. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Prog Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 31830503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional regulation of phospholipase D expression in cancer and inflammation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 15;289(33):22575-22582. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R114.569822. Epub 2014 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24990948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Physiological and pathophysiological roles for phospholipase D.J Lipid Res. 2015 Dec;56(12):2229-37. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R059220. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 25926691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key Disease Mechanisms Linked to Alzheimer's Disease in the Entorhinal Cortex.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 10;22(8):3915. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083915. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920138 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative lipidomic analysis of mouse and human brain with Alzheimer disease.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 20;287(4):2678-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.274142. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22134919 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D1 and D2 Synergistically Regulate Thrombus Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 22;21(18):6954. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186954. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32971863 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidic Acid: From Pleiotropic Functions to Neuronal Pathology.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jan 23;13:2. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00002. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30728767 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Almeida CG, Tampellini D, Takahashi RH, Greengard P, Lin MT, Snyder EM, Gouras GK. Beta-amyloid accumulation in APP mutant neurons reduces PSD-95 and GluR1 in synapses. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;20:187–198. - PubMed
-
- Bader MF, Vitale N. Phospholipase D in calcium-regulated exocytosis: lessons from chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1791:936–941. - PubMed
-
- Brandenburg LO, Konrad M, Wruck C, Koch T, Pufe T, Lucius R. Involvement of formyl-peptide-receptor-like-1 and phospholipase D in the internalization and signal transduction of amyloid beta 1–42 in glial cells. Neuroscience. 2008;156:266–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
