Stereo-selective inhibition of transient receptor potential TRPC5 cation channels by neuroactive steroids
- PMID: 21108630
- PMCID: PMC3057289
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01136.x
Stereo-selective inhibition of transient receptor potential TRPC5 cation channels by neuroactive steroids
Abstract
Background and purpose: Transient receptor potential canonical 5 (TRPC5) channels are widely expressed, including in the CNS, where they potentiate fear responses. They also contribute to other non-selective cation channels that are stimulated by G-protein-coupled receptor agonists and lipid and redox factors. Steroids are known to modulate fear and anxiety states, and we therefore investigated whether TRPC5 exhibited sensitivity to steroids.
Experimental approach: Human TRPC5 channels were conditionally expressed in HEK293 cells and studied using intracellular Ca2+ measurement, whole-cell voltage-clamp and excised patch techniques. For comparison, control experiments were performed with cells lacking TRPC5 channels or expressing another TRP channel, TRPM2. Native TRPC channel activity was recorded from vascular smooth muscle cells.
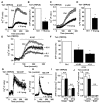
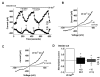
Key results: Extracellular application of pregnenolone sulphate, pregnanolone sulphate, pregnanolone, progesterone or dihydrotestosterone inhibited TRPC5 activity within 1-2min. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate or 17β-oestradiol had weak inhibitory effects. Pregnenolone, and allopregnanolone, a progesterone metabolite and stereo-isomer of pregnanolone, all had no effects. Progesterone was the most potent of the steroids, especially against TRPC5 channel activity evoked by sphingosine-1-phosphate. In outside-out patch recordings, bath-applied progesterone and dihydrotestosterone had strong and reversible effects, suggesting relatively direct mechanisms of action. Progesterone inhibited native TRPC5-containing channel activity, evoked by oxidized phospholipid.
Conclusions and implications: Our data suggest that TRPC5 channels are susceptible to relatively direct and rapid stereo-selective steroid modulation, leading to channel inhibition. The study adds to growing appreciation of TRP channels as non-genomic steroid sensors.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures





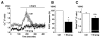
Similar articles
-
Pregnenolone sulphate-independent inhibition of TRPM3 channels by progesterone.Cell Calcium. 2012 Jan;51(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Cell Calcium. 2012. PMID: 22000496 Free PMC article.
-
GVI phospholipase A2 role in the stimulatory effect of sphingosine-1-phosphate on TRPC5 cationic channels.Cell Calcium. 2011 Oct;50(4):343-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Cell Calcium. 2011. PMID: 21742378 Free PMC article.
-
A sphingosine-1-phosphate-activated calcium channel controlling vascular smooth muscle cell motility.Circ Res. 2006 Jun 9;98(11):1381-9. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000225284.36490.a2. Epub 2006 May 4. Circ Res. 2006. PMID: 16675717 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC5.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:129-56. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_6. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756705 Review.
-
Bipolar phospholipid sensing by TRPC5 calcium channel.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Feb;35(Pt 1):101-4. doi: 10.1042/BST0350101. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17233612 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex hormone intake in female blood donors: impact on haemolysis during cold storage and regulation of erythrocyte calcium influx by progesterone.Blood Transfus. 2019 Jul;17(4):263-273. doi: 10.2450/2019.0053-19. Blood Transfus. 2019. PMID: 31385799 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxamido steroids inhibit the opening properties of transient receptor potential ion channels by lipid raft modulation.J Lipid Res. 2018 Oct;59(10):1851-1863. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M084723. Epub 2018 Aug 9. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 30093524 Free PMC article.
-
Neurosteroids, stress and depression: potential therapeutic opportunities.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013 Jan;37(1):109-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.10.005. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013. PMID: 23085210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPV2 is a novel biomarker and therapeutic target in triple negative breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 May 27;9(71):33459-33470. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9663. eCollection 2018 Sep 11. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 30323891 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of transient receptor potential canonical channels with lipids.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012 Feb;204(2):227-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02311.x. Epub 2011 May 27. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012. PMID: 21624095 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

