Peptides presented by HLA-DR molecules in synovia of patients with rheumatoid arthritis or antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis
- PMID: 21081667
- PMCID: PMC3047150
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M110.002477
Peptides presented by HLA-DR molecules in synovia of patients with rheumatoid arthritis or antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis
Abstract
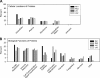
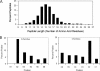
Disease-associated HLA-DR molecules, which may present autoantigens, constitute the greatest genetic risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis (LA). The peptides presented by HLA-DR molecules in synovia have not previously been defined. Using tandem mass spectrometry, rigorous database searches, and manual spectral interpretation, we identified 1,427 HLA-DR-presented peptides (220-464 per patient) from the synovia of four patients, two diagnosed with RA and two diagnosed with LA. The peptides were derived from 166 source proteins, including a wide range of intracellular and plasma proteins. A few epitopes were found only in RA or LA patients. However, two patients with different diseases who had the same HLA allele had the largest number of epitopes in common. In one RA patient, peptides were identified as originating from source proteins that have been reported to undergo citrullination under other circumstances, yet neither this post-translational modification nor anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies were detected. Instead, peptides with the post-translational modification of S-cysteinylation were identified. We conclude that a wide range of proteins enter the HLA-DR pathway of antigen-presenting cells in the patients' synovial tissue, and their HLA-DR genotype, not the disease type, appears to be the primary determinant of their HLA-DR-peptide repertoire. New insights into the naturally presented HLA-DR epitope repertoire in target tissues may allow the identification of pathogenic T cell epitopes, and this could lead to innovative therapeutic interventions.
Figures
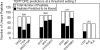


Similar articles
-
Immunogenic HLA-DR-Presented Self-Peptides Identified Directly from Clinical Samples of Synovial Tissue, Synovial Fluid, or Peripheral Blood in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis or Lyme Arthritis.J Proteome Res. 2017 Jan 6;16(1):122-136. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00386. Epub 2016 Nov 7. J Proteome Res. 2017. PMID: 27726376 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-10 is a target of T and B cell responses that correlate with synovial pathology in patients with antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis.J Autoimmun. 2016 May;69:24-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Feb 26. J Autoimmun. 2016. PMID: 26922382 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel, Immunogenic HLA-DR-Presented Prevotella copri Peptides in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Dec;73(12):2200-2205. doi: 10.1002/art.41807. Epub 2021 Oct 22. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34042327 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for the association between HLA DR4 and rheumatoid arthritis. From the shared epitope hypothesis to a peptidic model of rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Biochem. 1992 Jun;25(3):209-12. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(92)90328-p. Clin Biochem. 1992. PMID: 1378777 Review.
-
Autoimmune mechanisms in antibiotic treatment-resistant lyme arthritis.J Autoimmun. 2001 May;16(3):263-8. doi: 10.1006/jaut.2000.0495. J Autoimmun. 2001. PMID: 11334491 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Epitopes From Lyme Autoantigen Apolipoprotein B-100 and Borrelia burgdorferi Mcp4 in Murine Lyme Arthritis.J Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 14;230(Supplement_1):S27-S39. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae324. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39140726
-
HLA-DR-Expressing Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Are Inducible Antigen Presenting Cells That Present Autoantigens in Lyme Arthritis.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024 Oct;6(10):678-689. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11710. Epub 2024 Jul 27. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39073021 Free PMC article.
-
TRP14 is the rate-limiting enzyme for intracellular cystine reduction and regulates proteome cysteinylation.EMBO J. 2024 Jul;43(13):2789-2812. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00117-1. Epub 2024 May 29. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 38811853 Free PMC article.
-
Human leukocyte antigen HLA-DR-expressing fibroblast-like synoviocytes are inducible antigen presenting cells that present autoantigens in Lyme arthritis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 29:2023.11.21.568066. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.21.568066. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024 Oct;6(10):678-689. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11710. PMID: 38045407 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Autoimmunity to synovial extracellular matrix proteins in patients with postinfectious Lyme arthritis.J Clin Invest. 2023 Sep 1;133(17):e161170. doi: 10.1172/JCI161170. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37471146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steere A. C., Glickstein L. (2004) Elucidation of Lyme arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 143–152 - PubMed
-
- Steere A. C., Angelis S. M. (2006) Therapy for Lyme arthritis; strategies for the treatment of antibiotic-refractory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 3079–3086 - PubMed
-
- Steere A. C., Duray P. H., Butcher E. C. (1988) Spirochetal antigens and lymphoid cell surface markers in Lyme synovitis: comparison with rheumatoid synovium and tonsillar lymphoid tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 31, 487–495 - PubMed
-
- Takemura S., Braun A., Crowson C., Kurtin P. J., Cofield R. H., O'Fallon W. M., Goronzy J. J., Weyand C. M. (2001) Lymphoid neogenesis in rheumatoid synovitis. J. Immunol. 167, 1072–1080 - PubMed
-
- Deighton C. M., Walker D. J., Griffiths I. D., Roberts D. F. (1989) The contribution of HLA to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Genet. 36, 178–182 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

