Oxidation-induced intramolecular disulfide bond inactivates mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 by inhibiting ATP binding
- PMID: 21078955
- PMCID: PMC3000308
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1007225107
Oxidation-induced intramolecular disulfide bond inactivates mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 by inhibiting ATP binding
Abstract
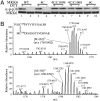
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 (MKK6) is a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MAP2K) subfamily that specifically phosphorylates and activates the p38 MAPKs. Based on both biochemical and cellular assays, we found that MKK6 was extremely sensitive to oxidation: It was inactivated by oxidation and its kinase activity was fully restored upon treatment with a reducing agent. Detailed mechanistic studies showed that cysteines 109 and 196, two of the six cysteines in MKK6, formed an intramolecular disulfide bond upon oxidation that inactivated MKK6 by inhibiting its ATP binding. This mechanism is distinct from that seen in other redox-sensitive kinases. The two cysteines involved in intramolecular disulfide formation are conserved in all seven members of the MAP2K family. Consistently, we confirmed that other MAP2Ks were also sensitive to oxidation. Our work reveals that MKK6 and other MAP2Ks are a distinct class of cellular redox sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


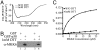

Similar articles
-
Stress-activated kinase pathway alteration is a frequent event in bladder cancer.Urol Oncol. 2012 Jul-Aug;30(4):415-20. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.03.002. Epub 2011 Dec 11. Urol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22154358
-
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 by human cytomegalovirus infection through two distinct pathways: a novel mechanism for activation of p38.J Virol. 2000 Feb;74(3):1158-67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.3.1158-1167.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10627526 Free PMC article.
-
MEK kinase 3 directly activates MKK6 and MKK7, specific activators of the p38 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 4;274(23):16604-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.23.16604. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10347227
-
Parallel regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 (MKK3) and MKK6 in Gq-signaling cascade.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 29;276(26):23362-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011752200. Epub 2001 Apr 13. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11304531
-
Alteration of an essential NK cell signaling pathway by low doses of tributyltin in human natural killer cells.Toxicology. 2006 Jul 25;224(3):229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.05.002. Epub 2006 Jun 14. Toxicology. 2006. PMID: 16781040
Cited by
-
Redox regulation of protein kinases.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Jul-Aug;48(4):332-56. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.790873. Epub 2013 May 3. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23639002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protocols and pitfalls in obtaining fatty acid-binding proteins for biophysical studies of ligand-protein and protein-protein interactions.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2017 May 4;10:318-324. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2017.05.001. eCollection 2017 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2017. PMID: 28955759 Free PMC article.
-
The bridge between cell survival and cell death: reactive oxygen species-mediated cellular stress.EXCLI J. 2023 Jun 22;22:520-555. doi: 10.17179/excli2023-6221. eCollection 2023. EXCLI J. 2023. PMID: 37534225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-induced oxidative stress and toxicity.J Toxicol. 2012;2012:645460. doi: 10.1155/2012/645460. Epub 2012 Aug 5. J Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22919381 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of reversible disulfide based on features from local structural signatures.BMC Genomics. 2017 Apr 4;18(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3668-8. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28376774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298:1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Eglen RM, Reisine T. The current status of drug discovery against the human kinome. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2009;7:22–43. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Karin M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature. 2001;410:37–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

