The plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of sorafenib after intravenous administration in non-human primates
- PMID: 21072558
- PMCID: PMC6636925
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-010-9585-1
The plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of sorafenib after intravenous administration in non-human primates
Abstract
Purpose: Sorafenib is a small molecule inhibitor of multiple signaling kinases thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of many tumors including brain tumors. Clinical trials with sorafenib in primary and metastatic brain tumors are ongoing. We evaluated the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pharmacokinetics (PK) of sorafenib after an intravenous (IV) dose in a non-human primate (NHP) model.
Methods: 7.3 mg/kg of sorafenib free base equivalent solubilized in 20% cyclodextrin was administered IV over 1 h to three adult rhesus monkeys. Serial paired plasma and CSF samples were collected over 24 h. Sorafenib was quantified with a validated HPLC/tandem mass spectrometry assay. PK parameters were estimated using non-compartmental methods. CSF penetration was calculated from the AUC(CSF) : AUC(plasma).
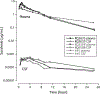
Results: Peak plasma concentrations after IV dosing ranged from 3.4 to 7.6 μg/mL. The mean ± standard deviation (SD) area under the plasma concentration from 0 to 24 h was 28 ± 4.3 μg • h/mL, which is comparable to the exposure observed in humans at recommended doses. The mean ± SD clearance was 1.7 ± 0.5 mL/min/kg. The peak CSF concentrations ranged from 0.00045 to 0.00058 μg/mL. The mean ± SD area under the CSF concentration from 0 to 24h was 0.0048 ± 0.0016 μg•h/mL. The mean CSF penetration of sorafenib was 0.02% and 3.4% after correcting for plasma protein binding.
Conclusion: Sorafenib is well tolerated in NHP and measurable in CSF after an IV dose. The CSF penetration of sorafenib is limited relative to total and free drug exposure in plasma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of the platinum analog satraplatin after intravenous administration in non-human primates.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;69(1):247-52. doi: 10.1007/s00280-011-1659-z. Epub 2011 Jun 26. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21706317 Free PMC article.
-
The plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of erlotinib and its active metabolite (OSI-420) after intravenous administration of erlotinib in non-human primates.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008 Aug;62(3):387-92. doi: 10.1007/s00280-007-0616-3. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17932674
-
Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of MP470 in non-human primates.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;67(4):809-12. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1380-3. Epub 2010 Jun 19. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20563581
-
Sorafenib: a review of its use in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Drugs. 2009;69(2):223-40. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969020-00006. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19228077 Review.
-
Sorafenib.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2006 Mar;7(4):453-61. doi: 10.1517/14656566.7.4.453. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 16503817 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase I trial, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of vandetanib and dasatinib in children with newly diagnosed diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 1;19(11):3050-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0306. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23536435 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development of a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic pediatric brain model for prediction of cerebrospinal fluid drug concentrations and the influence of meningitis.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Jun 13;15(6):e1007117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007117. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31194730 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Systemic Therapy Concurrent With Cranial Radiotherapy for Cerebral Metastases of Solid Tumors.Oncologist. 2017 Feb;22(2):222-235. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0117. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28167569 Free PMC article.
-
An Elusive Target: Inhibitors of JC Polyomavirus Infection and Their Development as Therapeutics for the Treatment of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 11;24(10):8580. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108580. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-Dose Sorafenib Acts as a Mitochondrial Uncoupler and Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Cell Metab. 2020 May 5;31(5):892-908.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.011. Cell Metab. 2020. PMID: 32375062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilhelm SM et al. (2004) BAY 43–9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64(19):7099–7109 - PubMed
-
- Lowy DR, Willumsen BM (1993) Function and regulation of ras. Annu Rev Biochem 62:851–891 - PubMed
-
- Rodenhuis S (1992) Ras and human tumors. Semin Cancer Biol 3 (4):241–247 - PubMed
-
- Satoh T, Kaziro Y (1992) Ras in signal transduction. Semin Cancer Biol 3(4):169–177 - PubMed
-
- Reuter CW, Morgan MA, Bergmann L (2000) Targeting the Ras signaling pathway: a rational, mechanism-based treatment for hematologic malignancies? Blood 96(5):1655–1669 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources