XLF regulates filament architecture of the XRCC4·ligase IV complex
- PMID: 21070942
- PMCID: PMC3008546
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2010.09.009
XLF regulates filament architecture of the XRCC4·ligase IV complex
Abstract
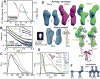
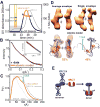
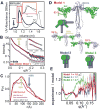
DNA ligase IV (LigIV) is critical for nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ), the major DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway in human cells, and LigIV activity is regulated by XRCC4 and XLF (XRCC4-like factor) interactions. Here, we employ small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) data to characterize three-dimensional arrangements in solution for full-length XRCC4, XRCC4 in complex with LigIV tandem BRCT domains and XLF, plus the XRCC4·XLF·BRCT2 complex. XRCC4 forms tetramers mediated through a head-to-head interface, and the XRCC4 C-terminal coiled-coil region folds back on itself to support this interaction. The interaction between XLF and XRCC4 is also mediated via head-to-head interactions. In the XLF·XRCC4·BRCT complex, alternating repeating units of XLF and XRCC4·BRCT place the BRCT domain on one side of the filament. Collective results identify XRCC4 and XLF filaments suitable to align DNA molecules and function to facilitate LigIV end joining required for DSB repair in vivo.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
XRCC4 and XLF form long helical protein filaments suitable for DNA end protection and alignment to facilitate DNA double strand break repair.Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;91(1):31-41. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2012-0058. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23442139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into the role of domain flexibility in human DNA ligase IV.Structure. 2012 Jul 3;20(7):1212-22. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.04.012. Epub 2012 May 31. Structure. 2012. PMID: 22658747 Free PMC article.
-
A human XRCC4-XLF complex bridges DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(4):1868-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks022. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22287571 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of the PNKP-XRCC4-LigIV DNA repair complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 2;45(10):6238-6251. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx275. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28453785 Free PMC article.
-
X-ray scattering reveals disordered linkers and dynamic interfaces in complexes and mechanisms for DNA double-strand break repair impacting cell and cancer biology.Protein Sci. 2021 Sep;30(9):1735-1756. doi: 10.1002/pro.4133. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 34056803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Repair of double-strand breaks by end joining.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 May 1;5(5):a012757. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012757. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23637284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the yeast DNA repair protein Nej1 in end processing during the repair of DNA double strand breaks by non-homologous end joining.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Jul;31:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 Apr 21. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25942368 Free PMC article.
-
XRCC4 and XLF form long helical protein filaments suitable for DNA end protection and alignment to facilitate DNA double strand break repair.Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;91(1):31-41. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2012-0058. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23442139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolution of complex ends by Nonhomologous end joining - better to be lucky than good?Genome Integr. 2012 Dec 31;3(1):10. doi: 10.1186/2041-9414-3-10. Genome Integr. 2012. PMID: 23276302 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Insights From Single-Molecule Studies of Repair of Double Strand Breaks.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 15;9:745311. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.745311. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34869333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahnesorg P, Smith P, Jackson SP. XLF interacts with the XRCC4-DNA ligase IV complex to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Cell. 2006;124:301–313. - PubMed
-
- Andres SN, Modesti M, Tsai CJ, Chu G, Junop MS. Crystal Structure of Human XLF: A Twist in Nonhomologous DNA End-Joining. Mol Cell. 2007;28:1093–1101. - PubMed
-
- Bernado P, Mylonas E, Petoukhov MV, Blackledge M, Svergun DI. Structural characterization of flexible proteins using small-angle X-ray scattering. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:5656–5664. - PubMed
-
- Buck D, Malivert L, de Chasseval R, Barraud A, Fondaneche MC, Sanal O, Plebani A, Stephan JL, Hufnagel M, le Deist F, et al. Cernunnos, a novel nonhomologous end-joining factor, is mutated in human immunodeficiency with microcephaly. Cell. 2006;124:287–299. - PubMed
-
- Callebaut I, Malivert L, Fischer A, Mornon JP, Revy P, de Villartay JP. Cernunnos interacts with the XRCC4 x DNA-ligase IV complex and is homologous to the yeast nonhomologous end-joining factor Nej1. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:13857–13860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

