Resonance assignments and secondary structure prediction of the As(III) metallochaperone ArsD in solution
- PMID: 21063813
- PMCID: PMC3364515
- DOI: 10.1007/s12104-010-9279-9
Resonance assignments and secondary structure prediction of the As(III) metallochaperone ArsD in solution
Abstract
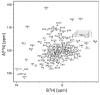
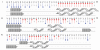
ArsD is a metallochaperone that delivers As(III) to the ArsA ATPase, the catalytic subunit of the ArsAB pump encoded by the arsRDABC operon of Escherichia coli plasmid R773. Conserved ArsD cysteine residues (Cys(12), Cys(13) and Cys(18)) construct the As(III) binding site of the protein, however a global structural understanding of this arsenic binding remains unclear. We have obtained NMR assignments for ArsD as a starting point for probing structural changes on the protein that occur in response to metalloid binding and upon formation of a complex with ArsA. The predicted solution structure of ArsD is in agreement with recently published crystallographic structural results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ArsD As(III) metallochaperone.Biometals. 2011 Jun;24(3):391-9. doi: 10.1007/s10534-010-9398-x. Epub 2010 Dec 25. Biometals. 2011. PMID: 21188475 Free PMC article.
-
ArsD residues Cys12, Cys13, and Cys18 form an As(III)-binding site required for arsenic metallochaperone activity.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jun 8;282(23):16783-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700886200. Epub 2007 Apr 17. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17439954
-
Arsenic binding and transfer by the ArsD As(III) metallochaperone.Biochemistry. 2010 May 4;49(17):3658-66. doi: 10.1021/bi100026a. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20361763 Free PMC article.
-
ArsD: an As(III) metallochaperone for the ArsAB As(III)-translocating ATPase.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2007 Dec;39(5-6):453-8. doi: 10.1007/s10863-007-9113-y. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2007. PMID: 17955352 Review.
-
Mechanisms of metalloregulation of an anion-translocating ATPase.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1995 Feb;27(1):85-91. doi: 10.1007/BF02110335. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1995. PMID: 7629056 Review.
Cited by
-
Arsenic binding to proteins.Chem Rev. 2013 Oct 9;113(10):7769-92. doi: 10.1021/cr300015c. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Chem Rev. 2013. PMID: 23808632 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Pathways of arsenic uptake and efflux.Curr Top Membr. 2012;69:325-58. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394390-3.00012-4. Curr Top Membr. 2012. PMID: 23046656 Free PMC article.
-
The ArsD As(III) metallochaperone.Biometals. 2011 Jun;24(3):391-9. doi: 10.1007/s10534-010-9398-x. Epub 2010 Dec 25. Biometals. 2011. PMID: 21188475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacharjee H, Rosen BP. Arsenic metabolism in prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes. In: Nies DH, Simon S, editors. Molecular microbiology of heavy metals. vol 6. Springer-Verlag; Heidelberg: 2007. pp. 371–406.
-
- Cavanagh J, Fairbrother WJ, Palmer AG, III, Skelton NJ. Protein NMR spectroscopy: principles and practice. Academic Press; San Diego: 1996.
-
- Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A. NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR. 1995;6:277–293. - PubMed
-
- Goddard TD, Kneller DG. SPARKY 3. University of California; San Francisco: 2001.
-
- Johnson BA. Using NMRView to visualize and analyze the NMR spectra of macromolecules. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;278:313–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

