Demonstration of angiotensin II-induced Ras activation in the trans-Golgi network and endoplasmic reticulum using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer-based biosensors
- PMID: 21062747
- PMCID: PMC3037644
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.176933
Demonstration of angiotensin II-induced Ras activation in the trans-Golgi network and endoplasmic reticulum using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer-based biosensors
Abstract
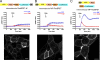
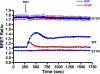
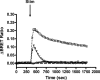
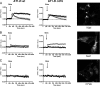
Previous studies have demonstrated that molecules of the Ras signaling pathway are present in intracellular compartments, including early endosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and the Golgi, and suggested that mitogens can regulate Ras activity in these endomembranes. In this study, we investigated the effect of angiotensin II (AngII) on intracellular Ras activity in living HEK293 cells expressing angiotensin type 1 receptors (AT(1)-Rs) using newly developed bioluminescence resonance energy transfer biosensors. To investigate the subcellular localization of AngII-induced Ras activation, we targeted our probes to various intracellular compartments, such as the trans-Golgi network (TGN), the ER, and early endosomes. Using these biosensors, we detected AngII-induced Ras activation in the TGN and ER, but not in early endosomes. In cells expressing a cytoplasmic tail deletion AT(1)-R mutant, the AngII-induced response was enhanced, suggesting that receptor internalization and β-arrestin binding are not required for AngII-induced Ras activation in endomembranes. Although we were able to demonstrate EGF-induced Ras activation in the plasma membrane and TGN, but not in other endomembranes, AG1478, an EGF receptor inhibitor, did not affect the AngII-induced response, suggesting that the latter is independent of EGF receptor transactivation. AngII was unable to stimulate Ras activity in the studied compartments in cells expressing a G protein coupling-deficient AT(1)-R mutant ((125)DRY(127) to (125)AAY(127)). These data suggest that AngII can stimulate Ras activity in the TGN and ER with a G protein-dependent mechanism, which does not require β-arrestin-mediated signaling, receptor internalization, and EGF receptor transactivation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mapping of the localization of type 1 angiotensin receptor in membrane microdomains using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer-based sensors.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 16;287(12):9090-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.293944. Epub 2012 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22291018 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor variants alter endosomal receptor-β-arrestin complex stability and MAPK activation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 18;295(38):13169-13180. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014330. Epub 2020 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32703898 Free PMC article.
-
The bile acid receptor TGR5 does not interact with β-arrestins or traffic to endosomes but transmits sustained signals from plasma membrane rafts.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 9;288(32):22942-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.455774. Epub 2013 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23818521 Free PMC article.
-
A century old renin-angiotensin system still grows with endless possibilities: AT1 receptor signaling cascades in cardiovascular physiopathology.Cell Signal. 2014 Oct;26(10):2147-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.06.011. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 25007996 Review.
-
Biased Agonism of the Angiotensin II Type I Receptor.Int Heart J. 2015;56(5):485-8. doi: 10.1536/ihj.15-256. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Int Heart J. 2015. PMID: 26180022 Review.
Cited by
-
Benefical therapeutic effect of Chinese Herbal Xinji'erkang formula on hypertension-induced renal injury in the 2-kidney-1-clip hypertensive rats.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014 Aug 23;11(5):16-27. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v11i5.3. eCollection 2014. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25395699 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical Detection of Diversity and Bias in GPCR Function.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Mar 5;5:26. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00026. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24634666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endomembrane H-Ras controls vascular endothelial growth factor-induced nitric-oxide synthase-mediated endothelial cell migration.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 24;288(21):15380-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.427765. Epub 2013 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23548900 Free PMC article.
-
The Diverse Roles of Arrestin Scaffolds in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling.Pharmacol Rev. 2017 Jul;69(3):256-297. doi: 10.1124/pr.116.013367. Pharmacol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28626043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma membrane phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and 4,5-bisphosphate determine the distribution and function of K-Ras4B but not H-Ras proteins.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 17;292(46):18862-18877. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.806679. Epub 2017 Sep 22. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28939768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takai Y., Sasaki T., Matozaki T. (2001) Physiol. Rev. 81, 153–208 - PubMed
-
- García-Mata R., Burridge K. (2007) Trends Cell Biol. 17, 36–43 - PubMed
-
- Buday L., Downward J. (2008) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1786, 178–187 - PubMed
-
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. (1993) Cell 74, 205–214 - PubMed
-
- Bivona T. G., Quatela S. E., Bodemann B. O., Ahearn I. M., Soskis M. J., Mor A., Miura J., Wiener H. H., Wright L., Saba S. G., Yim D., Fein A., Pérez de Castro I., Li C., Thompson C. B., Cox A. D., Philips M. R. (2006) Mol. Cell 21, 481–493 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

