Collagen binding specificity of the discoidin domain receptors: binding sites on collagens II and III and molecular determinants for collagen IV recognition by DDR1
- PMID: 21044884
- PMCID: PMC3034869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2010.10.004
Collagen binding specificity of the discoidin domain receptors: binding sites on collagens II and III and molecular determinants for collagen IV recognition by DDR1
Abstract
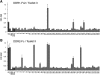
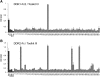
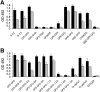
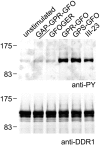
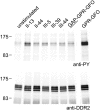
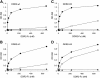
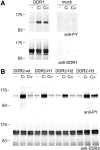
The discoidin domain receptors, DDR1 and DDR2 are cell surface receptor tyrosine kinases that are activated by triple-helical collagen. While normal DDR signalling regulates fundamental cellular processes, aberrant DDR signalling is associated with several human diseases. We previously identified GVMGFO (O is hydroxyproline) as a major DDR2 binding site in collagens I-III, and located two additional DDR2 binding sites in collagen II. Here we extend these studies to the homologous DDR1 and the identification of DDR binding sites on collagen III. Using sets of overlapping triple-helical peptides, the Collagen II and Collagen III Toolkits, we located several DDR2 binding sites on both collagens. The interaction of DDR1 with Toolkit peptides was more restricted, with DDR1 mainly binding to peptides containing the GVMGFO motif. Triple-helical peptides containing the GVMGFO motif induced DDR1 transmembrane signalling, and DDR1 binding and receptor activation occurred with the same amino acid requirements as previously defined for DDR2. While both DDRs exhibit the same specificity for binding the GVMGFO motif, which is present only in fibrillar collagens, the two receptors display distinct preferences for certain non-fibrillar collagens, with the basement membrane collagen IV being exclusively recognised by DDR1. Based on our recent crystal structure of a DDR2-collagen complex, we designed mutations to identify the molecular determinants for DDR1 binding to collagen IV. By replacing five amino acids in DDR2 with the corresponding DDR1 residues we were able to create a DDR2 construct that could function as a collagen IV receptor.
Copyright © 2010 International Society of Matrix Biology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
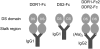

Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of collagen binding by the human discoidin domain receptors, DDR1 and DDR2. Identification of collagen binding sites in DDR2.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 9;278(19):16761-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301370200. Epub 2003 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12611880
-
Collagen recognition and transmembrane signalling by discoidin domain receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23128141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystallographic insight into collagen recognition by discoidin domain receptor 2.Structure. 2009 Dec 9;17(12):1573-1581. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2009.10.012. Structure. 2009. PMID: 20004161 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of high affinity binding motifs for the discoidin domain receptor DDR2 in collagen.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 14;283(11):6861-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709290200. Epub 2008 Jan 16. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18201965
-
Cell-collagen interactions: the use of peptide Toolkits to investigate collagen-receptor interactions.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Apr;36(Pt 2):241-50. doi: 10.1042/BST0360241. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18363567 Review.
Cited by
-
Bi-allelic Alterations in AEBP1 Lead to Defective Collagen Assembly and Connective Tissue Structure Resulting in a Variant of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.Am J Hum Genet. 2018 Apr 5;102(4):696-705. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.02.018. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Am J Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29606302 Free PMC article.
-
Multitasking discoidin domain receptors are involved in several and specific hallmarks of cancer.Cell Adh Migr. 2018;12(4):363-377. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2018.1465156. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Cell Adh Migr. 2018. PMID: 29701112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted collagen-DDR1 signaling in cancer.Trends Cell Biol. 2024 May;34(5):406-415. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.08.003. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Trends Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 37709651 Review.
-
Discoidin domain receptors: Micro insights into macro assemblies.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Nov;1866(11):118496. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.06.010. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31229648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discoidin domain receptor 2 mediates collagen-induced activation of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in human fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 21;292(16):6633-6643. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770057. Epub 2017 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28270508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdulhussein R., McFadden C., Fuentes-Prior P., Vogel W.F. Exploring the collagen-binding site of the DDR1 tyrosine kinase receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:31462–31470. - PubMed
-
- Alves F., Vogel W., Mossie K., Millauer B., Hofler H., Ullrich A. Distinct structural characteristics of discoidin I subfamily receptor tyrosine kinases and complementary expression in human cancer. Oncogene. 1995;10:609–618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

