Oxidative damage and TGF-β differentially induce lung epithelial cell sonic hedgehog and tenascin-C expression: implications for the regulation of lung remodelling in idiopathic interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 21039988
- PMCID: PMC3052752
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2010.00743.x
Oxidative damage and TGF-β differentially induce lung epithelial cell sonic hedgehog and tenascin-C expression: implications for the regulation of lung remodelling in idiopathic interstitial lung disease
Abstract
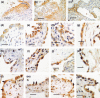
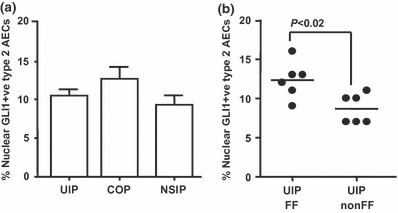
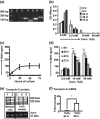
Idiopathic interstitial lung diseases (iILDs) are characterized by inflammation, hyperplasia of Type-II alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) and lung remodelling often with progressive fibrosis. It remains unclear which signals initiate iILD and/or maintain the disease processes. Using real-time RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry on archival biopsies of three patterns of iILD (usual interstitial pneumonitis/UIP, non-specific interstitial pneumonitis/NSIP and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia/COP) we investigated whether hedgehog signalling (previously associated with lung damage and repair) was functional and whether the damage associated extracellular matrix protein tenascin-C was present in activated Type-II AECs in all three iILDs. Using tissue culture, protein and mRNA detection we also determined how two signals (oxidative damage and TGF-β) associated with iILD pathogenesis affected Sonic hedgehog (SHH) and tenascin-C production by a Type-II AEC cell line. We report that SHH pathway and tenascin-C mRNA and proteins were found in UIP, NSIP and COP. SHH signalling was most active at sites of immature organizing fibrous tissue (fibroblastic foci) in UIP. In vitro Type-II AECs constitutively secrete SHH but not tenascin-C. Oxidative injury stimulated SHH release whereas TGF-β inhibited it. TGF-β and oxidative damage both upregulated tenascin-C mRNA but only TGF-β induced synthesis and release of a distinct protein isoform. SHH signalling is active in Type-II AECs from three types of ILD and all three express tenascin-C.
© 2010 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2010 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Figures
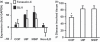

Similar articles
-
Tenascin immunoreactivity as a prognostic marker in usual interstitial pneumonia.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Aug;154(2 Pt 1):511-8. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.154.2.8756830. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996. PMID: 8756830
-
Expression of glutaredoxin is highly cell specific in human lung and is decreased by transforming growth factor-beta in vitro and in interstitial lung diseases in vivo.Hum Pathol. 2004 Aug;35(8):1000-7. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2004.04.009. Hum Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15297967
-
Differential epithelial expression of SHH and FOXF1 in usual and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia.Exp Mol Pathol. 2006 Apr;80(2):119-23. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2005.12.003. Epub 2006 Jan 30. Exp Mol Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16448649
-
Review series: Aspects of interstitial lung disease: connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: how does it differ from IPF? How should the clinical approach differ?Chron Respir Dis. 2011;8(1):53-82. doi: 10.1177/1479972310393758. Chron Respir Dis. 2011. PMID: 21339375 Review.
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling in the lung. From development to disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Jan;52(1):1-13. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0132TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25068457 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A genome-wide association meta-analysis implicates Hedgehog and Notch signaling in Dupuytren's disease.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 3;15(1):199. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44451-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38172110 Free PMC article.
-
CHIT1-positive microglia drive motor neuron ageing in the primate spinal cord.Nature. 2023 Dec;624(7992):611-620. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06783-1. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37907096
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanism of Pulmonary Fibrosis Post-COVID-19: Focus on Galectin-1, -3, -8, -9.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 26;23(15):8210. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158210. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog Signaling: Linking Embryonic Lung Development and Asthmatic Airway Remodeling.Cells. 2022 May 28;11(11):1774. doi: 10.3390/cells11111774. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant Multiciliogenesis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022 Aug;67(2):188-200. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0554OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35608953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn S, Joyner AL. In vivo analysis of quiescent adult neural stem cells responding to Sonic hedgehog. Nature. 2005;437:894–897. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000;161:646–664. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002;165:277–304. - PubMed
-
- Ask K, Martin GE, Kolb M, Gauldie J. Targeting genes for treatment in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: challenges and opportunities, promises and pitfalls. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006;3:389–393. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso WV, Lu J. Regulation of early lung morphogenesis: questions, facts and controversies. Development. 2006;133:1611–1624. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

