Diversity of human copy number variation and multicopy genes
- PMID: 21030649
- PMCID: PMC3020103
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1197005
Diversity of human copy number variation and multicopy genes
Abstract
Copy number variants affect both disease and normal phenotypic variation, but those lying within heavily duplicated, highly identical sequence have been difficult to assay. By analyzing short-read mapping depth for 159 human genomes, we demonstrated accurate estimation of absolute copy number for duplications as small as 1.9 kilobase pairs, ranging from 0 to 48 copies. We identified 4.1 million "singly unique nucleotide" positions informative in distinguishing specific copies and used them to genotype the copy and content of specific paralogs within highly duplicated gene families. These data identify human-specific expansions in genes associated with brain development, reveal extensive population genetic diversity, and detect signatures consistent with gene conversion in the human species. Our approach makes ~1000 genes accessible to genetic studies of disease association.
Figures
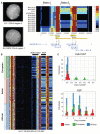

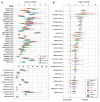
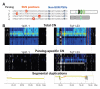

Comment in
-
Genomics. 1000 Genomes Project gives new map of genetic diversity.Science. 2010 Oct 29;330(6004):574-5. doi: 10.1126/science.330.6004.574. Science. 2010. PMID: 21030618 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Genomics. 1000 Genomes Project gives new map of genetic diversity.Science. 2010 Oct 29;330(6004):574-5. doi: 10.1126/science.330.6004.574. Science. 2010. PMID: 21030618 No abstract available.
-
Systematic inference of copy-number genotypes from personal genome sequencing data reveals extensive olfactory receptor gene content diversity.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Nov 11;6(11):e1000988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000988. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 21085617 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized copy number and segmental duplication maps using next-generation sequencing.Nat Genet. 2009 Oct;41(10):1061-7. doi: 10.1038/ng.437. Epub 2009 Aug 30. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19718026 Free PMC article.
-
Population genetic models of duplicated genes.Genetica. 2009 Sep;137(1):19-37. doi: 10.1007/s10709-009-9355-1. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Genetica. 2009. PMID: 19266289 Review.
-
An Evolutionary Perspective on the Impact of Genomic Copy Number Variation on Human Health.J Mol Evol. 2020 Jan;88(1):104-119. doi: 10.1007/s00239-019-09911-6. Epub 2019 Sep 14. J Mol Evol. 2020. PMID: 31522275 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic Multicopy Loci Targeted by Current Forensic Quantitative PCR Assays.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 5;15(10):1299. doi: 10.3390/genes15101299. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expansions contributing to human brain evolution.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 26:2024.09.26.615256. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.26.615256. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39386494 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Complex genetic variation in nearly complete human genomes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 25:2024.09.24.614721. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.24.614721. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39372794 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
CNVoyant a machine learning framework for accurate and explainable copy number variant classification.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 28;14(1):22411. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72470-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333267 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish models of human-duplicated SRGAP2 reveal novel functions in microglia and visual system development.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 27:2024.09.11.612570. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.11.612570. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39314374 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

