Fcγ receptors are required for NF-κB signaling, microglial activation and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in an AAV-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 20977765
- PMCID: PMC2975641
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-5-42
Fcγ receptors are required for NF-κB signaling, microglial activation and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in an AAV-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
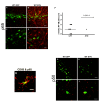
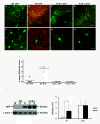
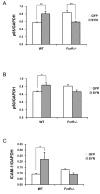
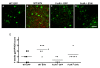
Overexpression of alpha-synuclein (α-SYN), a protein which plays an important role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD), triggers microglial activation and adaptive immune responses, and leads to neurodegeneration of dopaminergic (DA) neurons. We hypothesized a link between the humoral adaptive immune response and microglial activation in α-SYN induced neurodegeneration. To test this hypothesis, we employed adeno-associated virus serotype 2 (AAV2) to selectively over-express human α-SYN in the substantia nigra (SN) of wild-type mice and FcγR-/- mice, which lack high-affinity receptors for IgG. We found that in wild-type mice, α-SYN induced the expression of NF-κB p65 and pro-inflammatory molecules. In FcγR-/- mice, NF-κB activation was blocked and pro-inflammatory signaling was reduced. Microglial activation was examined using immunohistochemistry for gp91PHOX. At four weeks, microglia were strongly activated in wild-type mice, while microglial activation was attenuated in FcγR-/- mice. Dopaminergic neurodegeneration was examined using immunohistochemistry for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and unbiased stereology. α-SYN overexpression led to the appearance of dysmorphic neurites, and a loss of DA neurons in the SN in wild-type animals, while FcγR-/- mice did not exhibit neuritic change and were protected from α-SYN-induced neurodegeneration 24 weeks after injection. Our results suggest that the humoral adaptive immune response triggered by excess α-SYN plays a causative role in microglial activation through IgG-FcγR interaction. This involves NF-κB signaling, and leads to DA neurodegeneration. Therefore, blocking either FcγR signaling or specific intracellular signal transduction events downstream of FcγR-IgG interaction, such as NF-κB activation, may be viable therapeutic strategies in PD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The gamma chain subunit of Fc receptors is required for alpha-synuclein-induced pro-inflammatory signaling in microglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Nov 27;9:259. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-259. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 23186369 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of the class II transactivator attenuates inflammation and neurodegeneration in an alpha-synuclein model of Parkinson's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Aug 30;15(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1286-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30165873 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the JAK/STAT Pathway Protects Against α-Synuclein-Induced Neuroinflammation and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration.J Neurosci. 2016 May 4;36(18):5144-59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4658-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27147665 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Factor-κB Dysregulation and α-Synuclein Pathology: Critical Interplay in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Mar 24;12:68. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00068. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32265684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Microglial Activation: Implication in Parkinson's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Nov 16;13:768156. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.768156. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34867296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers and the Role of α-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Mar 23;13:645996. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.645996. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33833675 Free PMC article.
-
RNF11 modulates microglia activation through NF-κB signalling cascade.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Oct 24;528(2):174-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.08.060. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 22975135 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose inhalation exposure to trichloroethylene induces dopaminergic neurodegeneration in rodents.Toxicol Sci. 2023 Nov 28;196(2):218-228. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfad090. Toxicol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37669148 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the Fc gamma receptor in a chronic N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of dopaminergic loss.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 19;286(33):28783-28793. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.244830. Epub 2011 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21693708 Free PMC article.
-
Fractalkine Signaling Regulates the Inflammatory Response in an α-Synuclein Model of Parkinson Disease.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 15;10(10):e0140566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140566. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26469270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kruger R, Vieira-Saecker AM, Kuhn W, Berg D, Muller T, Kuhnl N, Fuchs GA, Storch A, Hungs M, Woitalla D, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O. Increased susceptibility to sporadic Parkinson's disease by a certain combined alpha-synuclein/apolipoprotein E genotype. Ann Neurol. 1999;45:611–7. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199905)45:5<611::AID-ANA9>3.0.CO;2-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997;276:2045–7. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5321.2045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurology. 1988;38:1285–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

