Flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase, reduces pancreatic damage in an experimental model of acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 20977452
- PMCID: PMC2998682
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00933.x
Flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase, reduces pancreatic damage in an experimental model of acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Acute pancreatitis is an autodigestive process resulting in acute inflammation of the pancreas. Accumulating evidence indicates the essential contribution of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) to acute pancreatitis. We studied the effects of flavocoxid, a plant-derived dual inhibitor of COX-2 and 5-LOX, in a model of caerulein (CER)-induced acute pancreatitis.
Experimental approach: Rats were given CER (80 µg·kg⁻¹ for each of four injections at hourly intervals) or vehicle (Sham-CER). Animals were then randomized to receive flavocoxid (20 mg·kg⁻¹ i.p.) or vehicle, 30 min after the first CER injection. Two hours after the last CER injection, we evaluated damage to the pancreas by histological methods; serum levels of amylase, lipase, leukotriene (LT)B₄ and prostaglandin (PG)E₂ ; pancreatic expression of COX-2 and 5-LOX and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) gene expression by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
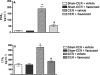
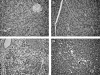
Key results: Caerulein induced inflammatory changes in the pancreas and raised values of the other variables measured. In CER-treated animals, but not in those given saline, flavocoxid inhibited COX-2 and 5-LOX expression, reduced serum levels of lipase and amylase and the degree of pancreatic oedema. Treatment with flavocoxid blunted the increased pancreatic TNF-α mRNA expression, serum leukotriene B₄ and prostaglandin E₂ levels, and protected against histological damage in terms of vacuolization and leukocyte infiltration.
Conclusions and implications: Our results confirm the key role of both COX-2 and 5-LOX in the inflammatory response to acute pancreatitis. Flavocoxid may provide a potential therapeutic approach to the treatment of patients at high risk of developing this life-threatening condition.
© 2010 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2010 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

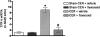

Similar articles
-
Use of a balanced dual cyclooxygenase-1/2 and 5-lypoxygenase inhibitor in experimental colitis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 15;789:152-162. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.07.033. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27450484
-
Effects of flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of COX and 5-lipoxygenase enzymes, on benign prostatic hyperplasia.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Sep;167(1):95-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01969.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. Retraction in: Br J Pharmacol. 2023 Aug;180(16):2189. doi: 10.1111/bph.16153 PMID: 22471974 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase, blunts pro-inflammatory phenotype activation in endotoxin-stimulated macrophages.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;157(8):1410-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00322.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19681869 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of eicosanoids in the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer: the roles of cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 21;20(31):10729-39. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10729. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25152576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetically-tailored and nature-derived dual COX-2/5-LOX inhibitors: Structural aspects and SAR.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Dec 5;225:113804. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113804. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34479036 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenic mechanisms of acute pancreatitis.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012 Sep;28(5):507-15. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e3283567f52. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22885948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavocoxid Ameliorates Aortic Calcification Induced by Hypervitaminosis D3 and Nicotine in Rats Via Targeting TNF-α, IL-1β, iNOS, and Osteogenic Runx2.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022 Dec;36(6):1047-1059. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07227-6. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022. PMID: 34309798
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of flavocoxid in high-cholesterol-fed rabbits.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;388(12):1333-44. doi: 10.1007/s00210-015-1168-4. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26341793
-
The effect of sulindac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, attenuates inflammation and fibrosis in a mouse model of chronic pancreatitis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug 24;12:115. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-115. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22920325 Free PMC article.
-
Flavocoxid inhibits phospholipase A2, peroxidase moieties of the cyclooxygenases (COX), and 5-lipoxygenase, modifies COX-2 gene expression, and acts as an antioxidant.Mediators Inflamm. 2011;2011:385780. doi: 10.1155/2011/385780. Epub 2011 Jun 19. Mediators Inflamm. 2011. PMID: 21765617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altavilla D, Famulari C, Passaniti M, Galeano M, Macrì A, Seminara P, et al. Attenuated caerulein-induced pancreatitis in nuclear factor-kappaB-deficient mice. Lab Invest. 2003a;83:1723–1732. - PubMed
-
- Altavilla D, Famulari C, Passaniti M, Campo GM, Macrì A, Seminara P, et al. Lipid peroxidation inhibition reduces NF-kappaB activation and attenuates caerulein-induced pancreatitis. Free Radic Res. 2003b;37:425–435. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia M, Brady M, Shokuhi S, Christmas S, Neoptolemos JP, Slavin J. Inflammatory mediators in acute pancreatitis. J Pathol. 2000;190:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia M, Wong FL, Cao Y, Lau HY, Huang J, Puneet P, et al. Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2005;5:132–144. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

