Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis
- PMID: 20944625
- PMCID: PMC3241506
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09513
Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis
Abstract
Vascular endothelial cells in the central nervous system (CNS) form a barrier that restricts the movement of molecules and ions between the blood and the brain. This blood-brain barrier (BBB) is crucial to ensure proper neuronal function and protect the CNS from injury and disease. Transplantation studies have demonstrated that the BBB is not intrinsic to the endothelial cells, but is induced by interactions with the neural cells. Owing to the close spatial relationship between astrocytes and endothelial cells, it has been hypothesized that astrocytes induce this critical barrier postnatally, but the timing of BBB formation has been controversial. Here we demonstrate that the barrier is formed during embryogenesis as endothelial cells invade the CNS and pericytes are recruited to the nascent vessels, over a week before astrocyte generation. Analysing mice with null and hypomorphic alleles of Pdgfrb, which have defects in pericyte generation, we demonstrate that pericytes are necessary for the formation of the BBB, and that absolute pericyte coverage determines relative vascular permeability. We demonstrate that pericytes regulate functional aspects of the BBB, including the formation of tight junctions and vesicle trafficking in CNS endothelial cells. Pericytes do not induce BBB-specific gene expression in CNS endothelial cells, but inhibit the expression of molecules that increase vascular permeability and CNS immune cell infiltration. These data indicate that pericyte-endothelial cell interactions are critical to regulate the BBB during development, and disruption of these interactions may lead to BBB dysfunction and neuroinflammation during CNS injury and disease.
Figures
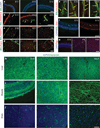
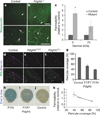
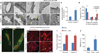
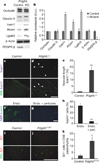
Comment in
-
Blood-brain barrier: Plugging the leak.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010 Dec;11(12):789. doi: 10.1038/nrn2954. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21132878 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Pericytes regulate the blood-brain barrier.Nature. 2010 Nov 25;468(7323):557-61. doi: 10.1038/nature09522. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20944627
-
CD146 coordinates brain endothelial cell-pericyte communication for blood-brain barrier development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Sep 5;114(36):E7622-E7631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710848114. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28827364 Free PMC article.
-
Mfsd2a is critical for the formation and function of the blood-brain barrier.Nature. 2014 May 22;509(7501):507-11. doi: 10.1038/nature13324. Epub 2014 May 14. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24828040 Free PMC article.
-
Targetability of the neurovascular unit in inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system.Immunol Rev. 2022 Oct;311(1):39-49. doi: 10.1111/imr.13121. Epub 2022 Jul 31. Immunol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35909222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of pericytes in the regulation of the neurovascular unit in health and disease.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;9(5):591-605. doi: 10.1007/s11481-014-9557-x. Epub 2014 Aug 14. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25119834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative analysis of the human brain mural cell transcriptome.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021 Nov;41(11):3052-3068. doi: 10.1177/0271678X211013700. Epub 2021 May 22. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021. PMID: 34027687 Free PMC article.
-
A CNS-specific hypomorphic Pdgfr-beta mutant model of diabetic retinopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 May 1;54(5):3569-78. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-11125. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23633653 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of hPSC-derived pericyte-like cells promotes functional recovery in ischemic stroke mice.Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 15;11(1):5196. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19042-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33060592 Free PMC article.
-
Focused ultrasound-mediated drug delivery through the blood-brain barrier.Expert Rev Neurother. 2015 May;15(5):477-91. doi: 10.1586/14737175.2015.1028369. Expert Rev Neurother. 2015. PMID: 25936845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Caveolin-1 and Junction Proteins by bFGF Contributes to the Integrity of Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier and Functional Recovery.Neurotherapeutics. 2016 Oct;13(4):844-858. doi: 10.1007/s13311-016-0437-3. Neurotherapeutics. 2016. PMID: 27170156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zlokovic BV. The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron. 2008;57:178–201. - PubMed
-
- Stewart PA, Wiley MJ. Developing nervous tissue induces formation of blood-brain barrier characteristics in invading endothelial cells: a study using quail-chick transplantation chimeras. Dev. Biol. 1981;84:183–192. - PubMed
-
- Janzer RC, Raff MC. Astrocytes induce blood-brain barrier properties in endothelial cells. Nature. 1987;325:253–257. - PubMed
-
- Bauer HC, et al. Neovascularization and the appearance of morphological characteristics of the blood-brain barrier in the embryonic mouse central nervous system. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1993;75:269–278. - PubMed
-
- Bolz S, Farrell CL, Dietz K, Wolburg H. Subcellular distribution of glucose transporter (GLUT-1) during development of the blood-brain barrier in rats. Cell Tissue Res. 1996;284:355–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

