Apolipoprotein E4 causes age- and Tau-dependent impairment of GABAergic interneurons, leading to learning and memory deficits in mice
- PMID: 20943911
- PMCID: PMC2988475
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4040-10.2010
Apolipoprotein E4 causes age- and Tau-dependent impairment of GABAergic interneurons, leading to learning and memory deficits in mice
Abstract
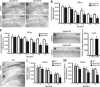
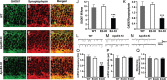
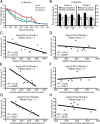
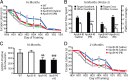
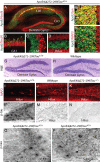
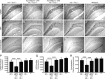
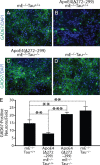
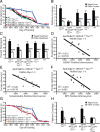
Apolipoprotein E4 (apoE4) is the major genetic risk factor for Alzheimer's disease. However, the underlying mechanisms are unclear. We found that female apoE4 knock-in (KI) mice had an age-dependent decrease in hilar GABAergic interneurons that correlated with the extent of learning and memory deficits, as determined in the Morris water maze, in aged mice. Treating apoE4-KI mice with daily peritoneal injections of the GABA(A) receptor potentiator pentobarbital at 20 mg/kg for 4 weeks rescued the learning and memory deficits. In neurotoxic apoE4 fragment transgenic mice, hilar GABAergic interneuron loss was even more pronounced and also correlated with the extent of learning and memory deficits. Neurodegeneration and tauopathy occurred earliest in hilar interneurons in apoE4 fragment transgenic mice; eliminating endogenous Tau prevented hilar GABAergic interneuron loss and the learning and memory deficits. The GABA(A) receptor antagonist picrotoxin abolished this rescue, while pentobarbital rescued learning deficits in the presence of endogenous Tau. Thus, apoE4 causes age- and Tau-dependent impairment of hilar GABAergic interneurons, leading to learning and memory deficits in mice. Consequently, reducing Tau and enhancing GABA signaling are potential strategies to treat or prevent apoE4-related Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein E4 causes age- and sex-dependent impairments of hilar GABAergic interneurons and learning and memory deficits in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053569. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300939 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing GABA Signaling during Middle Adulthood Prevents Age-Dependent GABAergic Interneuron Decline and Learning and Memory Deficits in ApoE4 Mice.J Neurosci. 2016 Feb 17;36(7):2316-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3815-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26888940 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4 Causes Age-Dependent Disruption of Slow Gamma Oscillations during Hippocampal Sharp-Wave Ripples.Neuron. 2016 May 18;90(4):740-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.04.009. Epub 2016 May 5. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27161522 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4 produced in GABAergic interneurons causes learning and memory deficits in mice.J Neurosci. 2014 Oct 15;34(42):14069-78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2281-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25319703 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4, inhibitory network dysfunction, and Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2019 Jun 11;14(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13024-019-0324-6. Mol Neurodegener. 2019. PMID: 31186040 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship between adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Oct;20(10):7369-7383. doi: 10.1002/alz.14179. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39166771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E4 causes age- and sex-dependent impairments of hilar GABAergic interneurons and learning and memory deficits in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053569. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300939 Free PMC article.
-
Hilar interneuron vulnerability distinguishes aged rats with memory impairment.J Comp Neurol. 2013 Oct 15;521(15):3508-23. doi: 10.1002/cne.23367. J Comp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23749483 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic Inhibitory Interneuron Deficits in Alzheimer's Disease: Implications for Treatment.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jun 30;14:660. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00660. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32714136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impairments of neural circuit function in Alzheimer's disease.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Aug 5;371(1700):20150429. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0429. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27377723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bareggi SR, Franceschi M, Bonini L, Zecca L, Smirne S. Decreased CSF concentrations of homovanillic acid and γ-aminobutyric acid in Alzheimer's disease. Age- or disease-related modifications? Arch Neurol. 1982;39:709–712. - PubMed
-
- Bour A, Grootendorst J, Vogel E, Kelche C, Dodart J-C, Bales K, Moreau P-H, Sullivan PM, Mathis C. Middle-aged human apoE4 targeted-replacement mice show retention deficits on a wide range of spatial memory tasks. Behav Brain Res. 2008;193:174–182. - PubMed
-
- Brosh I, Barkai E. Learning-induced enhancement of feedback inhibitory synaptic transmission. Learn Mem. 2009;16:413–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
