MiRNA-miRNA synergistic network: construction via co-regulating functional modules and disease miRNA topological features
- PMID: 20929877
- PMCID: PMC3035454
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq832
MiRNA-miRNA synergistic network: construction via co-regulating functional modules and disease miRNA topological features
Abstract
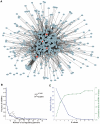
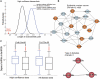
Synergistic regulations among multiple microRNAs (miRNAs) are important to understand the mechanisms of complex post-transcriptional regulations in humans. Complex diseases are affected by several miRNAs rather than a single miRNA. So, it is a challenge to identify miRNA synergism and thereby further determine miRNA functions at a system-wide level and investigate disease miRNA features in the miRNA-miRNA synergistic network from a new view. Here, we constructed a miRNA-miRNA functional synergistic network (MFSN) via co-regulating functional modules that have three features: common targets of corresponding miRNA pairs, enriched in the same gene ontology category and close proximity in the protein interaction network. Predicted miRNA synergism is validated by significantly high co-expression of functional modules and significantly negative regulation to functional modules. We found that the MFSN exhibits a scale free, small world and modular architecture. Furthermore, the topological features of disease miRNAs in the MFSN are distinct from non-disease miRNAs. They have more synergism, indicating their higher complexity of functions and are the global central cores of the MFSN. In addition, miRNAs associated with the same disease are close to each other. The structure of the MFSN and the features of disease miRNAs are validated to be robust using different miRNA target data sets.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Risk miRNA screening of ovarian cancer based on miRNA functional synergistic network.J Ovarian Res. 2014 Jan 21;7:9. doi: 10.1186/1757-2215-7-9. J Ovarian Res. 2014. Retraction in: J Ovarian Res. 2015 Mar 26;8(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13048-015-0145-3. PMID: 24444095 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A network analysis of miRNA mediated gene regulation of rice: crosstalk among biological processes.Mol Biosyst. 2015 Aug;11(8):2273-80. doi: 10.1039/c5mb00222b. Mol Biosyst. 2015. PMID: 26066638
-
Identification of lung cancer miRNA-miRNA co-regulation networks through a progressive data refining approach.J Theor Biol. 2015 Sep 7;380:271-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.05.025. Epub 2015 May 28. J Theor Biol. 2015. PMID: 26026830
-
Survey of miRNA-miRNA cooperative regulation principles across cancer types.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Sep 27;20(5):1621-1638. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby038. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29800060 Review.
-
MicroRNAs--regulators of signaling networks in dilated cardiomyopathy.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010 Jun;3(3):225-34. doi: 10.1007/s12265-010-9177-7. Epub 2010 May 1. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010. PMID: 20560044 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole miRNome-wide differential co-expression of microRNAs.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012 Oct;10(5):285-94. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23200138 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive ceRNA-ceRNA interaction networks mediated by miRNAs regulate development in multiple rhesus tissues.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Nov 2;44(19):9438-9451. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw587. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27365046 Free PMC article.
-
Dissection of protein interactomics highlights microRNA synergy.PLoS One. 2013 May 14;8(5):e63342. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063342. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691029 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying miRNA synergism using multiple-intervention causal inference.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Dec 27;20(Suppl 23):613. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-3215-5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31881825 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Properties of Human Breast Milk: MicroRNA Contents and Potential Epigenetic Effects.Biomedicines. 2022 May 24;10(6):1219. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061219. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740242 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Farh KK, Grimson A, Jan C, Lewis BP, Johnston WK, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science. 2005;310:1817–1821. - PubMed
-
- Migliore C, Giordano S. MiRNAs as new master players. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:2185–2186. - PubMed
-
- Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:766–770. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 2003;115:787–798. - PubMed

