STIM1-dependent and STIM1-independent function of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) channels tunes their store-operated mode
- PMID: 20926378
- PMCID: PMC2992299
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.155036
STIM1-dependent and STIM1-independent function of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) channels tunes their store-operated mode
Abstract
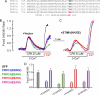
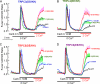
Ca(2+) influx by store-operated Ca(2+) channels is a key component of the receptor-evoked Ca(2+) signal. In all cells examined, transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) channels mediate a significant portion of the receptor-stimulated Ca(2+) influx. Recent studies have revealed how STIM1 activates TRPC1 in response to store depletion; however, the role of STIM1 in TRPC channel activation by receptor stimulation is not fully understood. Here, we established mutants of TRPC channels that could not be activated by STIM1 but were activated by the "charge-swap" mutant STIM1(K684E,K685E). Significantly, WT but not mutant TRPC channels were inhibited by scavenging STIM1 with Orai1(R91W), indicating the STIM1 dependence and independence of WT and mutant TRPC channels, respectively. Importantly, mutant TRPC channels were robustly activated by receptor stimulation. Moreover, STIM1 and STIM1(K684E,K685E) reciprocally affected receptor-activated WT and mutant TRPC channels. Together, these findings indicate that TRPC channels can function as STIM1-dependent and STIM1-independent channels, which increases the versatility of TRPC channel function and their role in receptor-stimulated Ca(2+) influx.
Figures

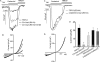
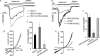

Similar articles
-
Molecular determinants mediating gating of Transient Receptor Potential Canonical (TRPC) channels by stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1).J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):6372-6382. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.546556. Epub 2014 Jan 24. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24464579 Free PMC article.
-
The polybasic lysine-rich domain of plasma membrane-resident STIM1 is essential for the modulation of store-operated divalent cation entry by extracellular calcium.Cell Signal. 2013 May;25(5):1328-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.01.025. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23395841
-
The Ca(2+) sensor stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) is necessary and sufficient for the store-operated Ca(2+) entry function of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) 1 and 4 channels in endothelial cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;81(4):510-26. doi: 10.1124/mol.111.074658. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22210847 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC channels as STIM1-regulated SOCs.Channels (Austin). 2009 Jul-Aug;3(4):221-5. doi: 10.4161/chan.3.4.9198. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Channels (Austin). 2009. PMID: 19574740 Review.
-
TRPC Channels in the SOCE Scenario.Cells. 2020 Jan 5;9(1):126. doi: 10.3390/cells9010126. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31948094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Store-operated Ca2+ entry in primary murine lung fibroblasts is independent of classical transient receptor potential (TRPC) channels and contributes to cell migration.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 22;10(1):6812. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63677-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32321939 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC5 channel sensitivities to antioxidants and hydroxylated stilbenes.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 18;286(7):5078-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.196956. Epub 2010 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21127073 Free PMC article.
-
Orai1 and CRAC channel dependence of VEGF-activated Ca2+ entry and endothelial tube formation.Circ Res. 2011 May 13;108(10):1190-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243352. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21441136 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of TRPC4 regulation by calmodulin and pharmacological agents.Elife. 2020 Nov 25;9:e60603. doi: 10.7554/eLife.60603. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33236980 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of STIM1 by phosphorylation.Commun Integr Biol. 2013 Nov 1;6(6):e26283. doi: 10.4161/cib.26283. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Commun Integr Biol. 2013. PMID: 24505502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

