The redox basis of epigenetic modifications: from mechanisms to functional consequences
- PMID: 20919933
- PMCID: PMC3118659
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3492
The redox basis of epigenetic modifications: from mechanisms to functional consequences
Abstract
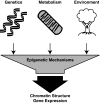
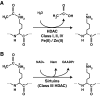
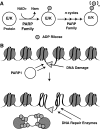
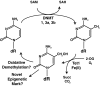
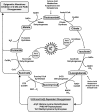
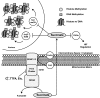
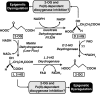
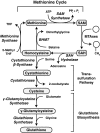
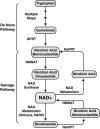
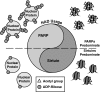
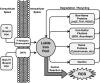
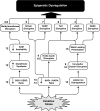
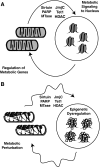
Epigenetic modifications represent mechanisms by which cells may effectively translate multiple signaling inputs into phenotypic outputs. Recent research is revealing that redox metabolism is an increasingly important determinant of epigenetic control that may have significant ramifications in both human health and disease. Numerous characterized epigenetic marks, including histone methylation, acetylation, and ADP-ribosylation, as well as DNA methylation, have direct linkages to central metabolism through critical redox intermediates such as NAD(+), S-adenosyl methionine, and 2-oxoglutarate. Fluctuations in these intermediates caused by both normal and pathologic stimuli may thus have direct effects on epigenetic signaling that lead to measurable changes in gene expression. In this comprehensive review, we present surveys of both metabolism-sensitive epigenetic enzymes and the metabolic processes that may play a role in their regulation. To close, we provide a series of clinically relevant illustrations of the communication between metabolism and epigenetics in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer disease, cancer, and environmental toxicity. We anticipate that the regulatory mechanisms described herein will play an increasingly large role in our understanding of human health and disease as epigenetics research progresses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Perspectives on the interactions between metabolism, redox, and epigenetics in plants.J Exp Bot. 2016 Oct;67(18):5291-5300. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw310. Epub 2016 Aug 16. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27531885 Review.
-
Redox Components: Key Regulators of Epigenetic Modifications in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 19;21(4):1419. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041419. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32093110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox regulation of chromatin remodelling in plants.Plant Cell Environ. 2024 Aug;47(8):2780-2792. doi: 10.1111/pce.14843. Epub 2024 Feb 4. Plant Cell Environ. 2024. PMID: 38311877 Review.
-
Metabolic regulation of the plant epigenome.Plant J. 2023 Jun;114(5):1001-1013. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16122. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Plant J. 2023. PMID: 36705504 Review.
-
Metabolism and epigenetics.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2015;31:473-496. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100814-125544. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26359776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of redox signaling in epigenetics and cardiovascular disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 May 20;18(15):1920-36. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4926. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 23480168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-induced signaling in the cardiovascular system: pathogenesis and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Nov 20;8(1):431. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01652-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37981648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo evidence of ascorbate involvement in the generation of epigenetic DNA modifications in leukocytes from patients with colorectal carcinoma, benign adenoma and inflammatory bowel disease.J Transl Med. 2018 Jul 20;16(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1581-9. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30029654 Free PMC article.
-
Amino Acid Catabolism: An Overlooked Area of Metabolism.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 29;15(15):3378. doi: 10.3390/nu15153378. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tobacco carcinogen 4-[methyl(nitroso)amino]-1-(3-pyridinyl)-1-butanone (NNK) drives metabolic rewiring and epigenetic reprograming in A/J mice lung cancer model and prevention with diallyl sulphide (DAS).Carcinogenesis. 2022 Mar 24;43(2):140-149. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgab119. Carcinogenesis. 2022. PMID: 34888630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackrell BA. Cytopathies involving mitochondrial complex II. Mol Aspects Med. 2002;23:369–384. - PubMed
-
- Aghili M. Zahedi F. Rafiee E. Hydroxyglutaric aciduria and malignant brain tumor: a case report and literature review. J Neurooncol. 2009;91:233–236. - PubMed
-
- Ahringer J. NuRD and SIN3 histone deacetylase complexes in development. Trends Genet. 2000;16:351–356. - PubMed
-
- Allis CD. Berger SL. Cote J. Dent S. Jenuwien T. Kouzarides T. Pillus L. Reinberg D. Shi Y. Shiekhattar R, et al. New nomenclature for chromatin-modifying enzymes. Cell. 2007;131:633–636. - PubMed
-
- Althaus FR. Hofferer L. Kleczkowska HE. Malanga M. Naegeli H. Panzeter PL. Realini CA. Histone shuttling by poly ADP-ribosylation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1994;138:53–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

