Dysregulation of the mTOR pathway mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20862226
- PMCID: PMC2942840
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012845
Dysregulation of the mTOR pathway mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is an evolutionarily conserved Ser/Thr protein kinase that plays a pivotal role in multiple fundamental biological processes, including synaptic plasticity. We explored the relationship between the mTOR pathway and β-amyloid (Aβ)-induced synaptic dysfunction, which is considered to be critical in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
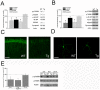
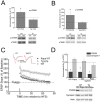
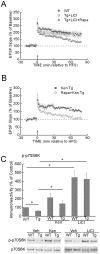
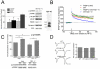
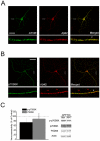
Methodology/principal findings: We provide evidence that inhibition of mTOR signaling correlates with impairment in synaptic plasticity in hippocampal slices from an AD mouse model and in wild-type slices exposed to exogenous Aβ1-42. Importantly, by up-regulating mTOR signaling, glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) inhibitors rescued LTP in the AD mouse model, and genetic deletion of FK506-binding protein 12 (FKBP12) prevented Aβ-induced impairment in long-term potentiation (LTP). In addition, confocal microscopy demonstrated co-localization of intraneuronal Aβ42 with mTOR.
Conclusions/significance: These data support the notion that the mTOR pathway modulates Aβ-related synaptic dysfunction in AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
REDD1 Is Involved in Amyloid β-Induced Synaptic Dysfunction and Memory Impairment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 13;21(24):9482. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249482. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33322202 Free PMC article.
-
The flavonoid baicalein rescues synaptic plasticity and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Sep 15;311:309-321. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.05.052. Epub 2016 May 24. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27233830
-
The ketamine metabolite (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine rescues hippocampal mRNA translation, synaptic plasticity and memory in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Aug;20(8):5398-5410. doi: 10.1002/alz.14034. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 38934107 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Alterations in Mouse Models for Alzheimer Disease-A Special Focus on N-Truncated Abeta 4-42.Molecules. 2018 Mar 21;23(4):718. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040718. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29561816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the nitric oxide pathway in synaptic dysfunction following amyloid elevation in Alzheimer's disease.Rev Neurosci. 2006;17(5):497-523. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2006.17.5.497. Rev Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17180876 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of mTOR: a culprit of Alzheimer's disease?Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015 Apr 9;11:1015-30. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S75717. eCollection 2015. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015. PMID: 25914534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spines, plasticity, and cognition in Alzheimer's model mice.Neural Plast. 2012;2012:319836. doi: 10.1155/2012/319836. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Neural Plast. 2012. PMID: 22203915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pain-Relieving Effects of mTOR Inhibitor in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex of Neuropathic Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Apr;56(4):2482-2494. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1245-z. Epub 2018 Jul 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30032425 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol hexakisphosphate kinases induce cell death in Huntington disease.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 29;286(30):26680-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.220749. Epub 2011 Jun 7. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21652713 Free PMC article.
-
G-Protein Coupled Receptor Signaling and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 Regulation.Mol Pharmacol. 2022 Apr;101(4):181-190. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.121.000302. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Mol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34965982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haass C, Selkoe DJ. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:329–344. - PubMed
-
- Oddo S, Caccamo A, Shepherd JD, Murphy MP, Golde TE, et al. Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease with plaques and tangles: intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron. 2003;39:409–421. - PubMed
-
- Yang Q, Guan K-L. Expanding mTOR signaling. Cell Res. 2007;17:666–681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS034007/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM054508/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG009464/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS034007/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R29 NS034007/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AG028174/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG09464/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG027140/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020729/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027140/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG28174/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM054508/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS034007/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

