Diminished contact-dependent reinforcement of Syk activation underlies impaired thrombus growth in mice lacking Semaphorin 4D
- PMID: 20855865
- PMCID: PMC3031415
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-279943
Diminished contact-dependent reinforcement of Syk activation underlies impaired thrombus growth in mice lacking Semaphorin 4D
Abstract
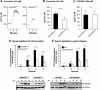
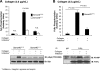
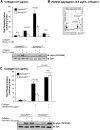
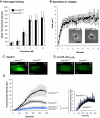
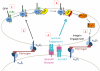
We recently reported that Semaphorin 4D (Sema4D) and its receptors are expressed on the platelet surface and showed that Sema4D((-/-)) mice have a selective defect in collagen-induced platelet aggregation and an impaired vascular injury response. Here we investigated the mechanisms involved, tested the role of platelet-platelet contacts in Sema4D-mediated events, and examined the relationship between Sema4D-dependent signaling and integrin α(IIb)β(3) outside-in signaling. The results show that spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) activation, an early step in collagen signaling via the glycoprotein VI (GPVI)/FcRγ complex, is greatly reduced in Sema4D((-/-)) platelets and can be restored by adding soluble Sema4D. Earlier events, including FcRγ phosphorylation, occur normally; later events are impaired. In contrast, when engagement of α(IIb)β(3) was blocked, Sema4D((-/-)) and control platelets were indistinguishable in assays of Syk activation, adhesion, spreading on collagen, and activation of α(IIb)β(3). Finally, we found that, unlike the Sema4D knockout, α(IIb)β(3) blockade inhibited FcRγ phosphorylation and that stimulating aggregation with Mn(2+) failed to normalize Syk activation in the absence of Sema4D. Collectively, these results show that α(IIb)β(3) and Sema4D jointly promote collagen responses by amplifying Syk activation, partly by forming integrin-mediated contacts that enable the binding of Sema4D to its receptors and partly through integrin outside-in signaling. These 2 processes are interdependent, but distinguishable.
Figures
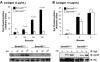
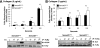
Similar articles
-
Distinct contributions of glycoprotein VI and alpha(2)beta(1) integrin to the induction of platelet protein tyrosine phosphorylation and aggregation.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000 Feb 15;374(2):356-62. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1627. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 10666318
-
CEACAM2 negatively regulates hemi (ITAM-bearing) GPVI and CLEC-2 pathways and thrombus growth in vitro and in vivo.Blood. 2014 Oct 9;124(15):2431-41. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-569707. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25085348 Free PMC article.
-
The alpha2beta1 integrin is a necessary co-receptor for collagen-induced activation of Syk and the subsequent phosphorylation of phospholipase Cgamma2 in platelets.J Biol Chem. 1996 Oct 25;271(43):26668-76. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8900143
-
Platelet receptors and signaling in the dynamics of thrombus formation.Haematologica. 2009 May;94(5):700-11. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2008.003178. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Haematologica. 2009. PMID: 19286885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semaphorin 4D as a guidance molecule in the immune system.Int Rev Immunol. 2021;40(4):268-273. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2021.1905807. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Int Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33787446 Review.
Cited by
-
The use of microfluidics in hemostasis: clinical diagnostics and biomimetic models of vascular injury.Curr Opin Hematol. 2013 Sep;20(5):417-23. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3283642186. Curr Opin Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23872531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet formation and activation are influenced by neuronal guidance proteins.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 15;14:1206906. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1206906. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37398659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal guidance proteins in cardiovascular inflammation.Basic Res Cardiol. 2021 Jan 29;116(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s00395-021-00847-x. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33511463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mice lacking the SLAM family member CD84 display unaltered platelet function in hemostasis and thrombosis.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 31;9(12):e115306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115306. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25551754 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping the platelet response to vascular injury.Curr Opin Hematol. 2014 Sep;21(5):410-7. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000070. Curr Opin Hematol. 2014. PMID: 25023471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Suzuki K, Kumanogoh A, Kikutani H. Semaphorins and their receptors in immune cell interactions. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(1):17–23. - PubMed
-
- Tamagnone L, Artigiani S, Chen H, et al. Plexins are a large family of receptors for transmembrane, secreted, and GPI-anchored semaphorins in vertebrates. Cell. 1999;99(1):71–80. - PubMed
-
- Basile JR, Barac A, Zhu T, Guan KL, Gutkind JS. Class IV semaphorins promote angiogenesis by stimulating Rho-initiated pathways through plexin-B. Cancer Res. 2004;64(15):5212–5224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

