Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1: a serial clearance homeostatic mechanism controlling Alzheimer's amyloid β-peptide elimination from the brain
- PMID: 20854368
- PMCID: PMC2972355
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07002.x
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1: a serial clearance homeostatic mechanism controlling Alzheimer's amyloid β-peptide elimination from the brain
Abstract
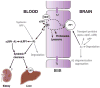
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1), a member of the low-density lipoprotein receptor family, has major roles in the cellular transport of cholesterol, endocytosis of 40 structurally diverse ligands, transcytosis of ligands across the blood-brain barrier, and transmembrane and nuclear signaling. Recent evidence indicates that LRP1 regulates brain and systemic clearance of Alzheimer's disease (AD) amyloid β-peptide (Aβ). According to the two-hit vascular hypothesis for AD, vascular damage precedes cerebrovascular and brain Aβ accumulation (hit 1) which then further amplifies neurovascular dysfunction (hit 2) preceding neurodegeneration. In this study, we discuss the roles of LRP1 during the hit 1 and hit 2 stage of AD pathogenesis and describe a three-level serial LRP1-dependent homeostatic control of Aβ clearance including (i) cell-surface LRP1 at the blood-brain barrier and cerebrovascular cells mediating brain-to-blood Aβ clearance (ii) circulating LRP1 providing a key endogenous peripheral 'sink' activity for plasma Aβ which prevents free Aβ access to the brain, and (iii) LRP1 in the liver mediating systemic Aβ clearance. Pitfalls in experimental Aβ brain clearance measurements with the concurrent use of peptides/proteins such as receptor-associated protein and aprotinin are also discussed. We suggest that LRP1 has a critical role in AD pathogenesis and is an important therapeutic target in AD.
© 2010 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry © 2010 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1: a physiological Aβ homeostatic mechanism with multiple therapeutic opportunities.Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Oct;136(1):94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.07.008. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22820095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocytic LRP1 Mediates Brain Aβ Clearance and Impacts Amyloid Deposition.J Neurosci. 2017 Apr 12;37(15):4023-4031. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3442-16.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 8. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28275161 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of ADAM10 promotes the clearance of Aβ across the BBB by reducing LRP1 ectodomain shedding.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016 Aug 8;13(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12987-016-0038-x. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016. PMID: 27503326 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the blood-brain barrier in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007 Apr;4(2):191-7. doi: 10.2174/156720507780362245. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007. PMID: 17430246 Review.
-
LRP1 in brain vascular smooth muscle cells mediates local clearance of Alzheimer's amyloid-β.J Neurosci. 2012 Nov 14;32(46):16458-65. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3987-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23152628 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease.Nat Rev Neurol. 2015 Aug;11(8):457-70. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26195256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insoluble Vascular Amyloid Deposits Trigger Disruption of the Neurovascular Unit in Alzheimer's Disease Brains.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 1;22(7):3654. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073654. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33915754 Free PMC article.
-
How Do Meningeal Lymphatic Vessels Drain the CNS?Trends Neurosci. 2016 Sep;39(9):581-586. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Trends Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27460561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Glia in Wilson's Disease: Clinical, Neuroimaging, Neuropathological and Molecular Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7545. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147545. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 17;16(7):948. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070948. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065645 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arelin K, Kinoshita A, Whelan CM, Irizarry MC, Rebeck GW, Strickland DK, Hyman BT. LRP and senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease: colocalization with apolipoprotein E and with activated astrocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2002;104:38–46. - PubMed
-
- Bading JR, Yamada S, Mackic JB, Kirkman L, Miller C, Calero M, Ghiso J, Frangione B, Zlokovic BV. Brain clearance of Alzheimer's amyloid-beta40 in the squirrel monkey: a SPECT study in a primate model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J Drug Target. 2002;10:359–368. - PubMed
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:663–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

