Escherichia coli RecBC helicase has two translocase activities controlled by a single ATPase motor
- PMID: 20852646
- PMCID: PMC2950890
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1901
Escherichia coli RecBC helicase has two translocase activities controlled by a single ATPase motor
Abstract
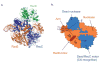
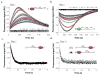
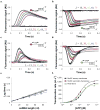
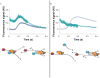
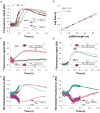
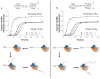
E. coli RecBCD is a DNA helicase with two ATPase motors (RecB, a 3'→5' translocase, and RecD, a 5'→3' translocase) that function in repair of double-stranded DNA breaks. The RecBC heterodimer, with only the RecB motor, remains a processive helicase. Here we examined RecBC translocation along single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). Notably, we found RecBC to have two translocase activities: the primary translocase moves 3'→5', whereas the secondary translocase moves RecBC along the opposite strand of a forked DNA at a similar rate. The secondary translocase is insensitive to the ssDNA backbone polarity, and we propose that it may fuel RecBCD translocation along double-stranded DNA ahead of the unwinding fork and ensure that the unwound single strands move through RecBCD at the same rate after interaction with a crossover hot-spot indicator (Chi) sequence.
Figures
Comment in
-
One motor driving two translocases.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Oct;17(10):1166-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1010-1166. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20924403
Similar articles
-
Asymmetric regulation of bipolar single-stranded DNA translocation by the two motors within Escherichia coli RecBCD helicase.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 11;288(2):1055-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.423384. Epub 2012 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23192341 Free PMC article.
-
One motor driving two translocases.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Oct;17(10):1166-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1010-1166. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20924403
-
The primary and secondary translocase activities within E. coli RecBC helicase are tightly coupled to ATP hydrolysis by the RecB motor.J Mol Biol. 2012 Oct 26;423(3):303-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.07.009. Epub 2012 Jul 20. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22820092 Free PMC article.
-
Chi and the RecBC D enzyme of Escherichia coli.Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:49-70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.28.120194.000405. Annu Rev Genet. 1994. PMID: 7893137 Review.
-
The nucleotide excision repair protein UvrB, a helicase-like enzyme with a catch.Mutat Res. 2000 Aug 30;460(3-4):277-300. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(00)00032-x. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10946234 Review.
Cited by
-
A new twist on PIFE: photoisomerisation-related fluorescence enhancement.Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2023 Oct 12;12(1):012001. doi: 10.1088/2050-6120/acfb58. Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2023. PMID: 37726007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Auxiliary ATP binding sites support DNA unwinding by RecBCD.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 4;13(1):1806. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29387-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35379800 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric regulation of bipolar single-stranded DNA translocation by the two motors within Escherichia coli RecBCD helicase.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 11;288(2):1055-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.423384. Epub 2012 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23192341 Free PMC article.
-
Recombination hotspots attenuate the coupled ATPase and translocase activities of an AddAB-type helicase-nuclease.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 May;42(9):5633-43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku188. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24682829 Free PMC article.
-
Translocation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pif1 helicase monomers on single-stranded DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr;41(8):4613-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt117. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23446274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singleton MR, Dillingham MS, Wigley DB. Structure and Mechanism of Helicases and Nucleic Acid Translocases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:23–50. - PubMed
-
- Dillingham MS, Spies M, Kowalczykowski SC. RecBCD enzyme is a bipolar DNA helicase. Nature. 2003;423:893–897. - PubMed
-
- Taylor AF, Smith GR. RecBCD enzyme is a DNA helicase with fast and slow motors of opposite polarity. Nature. 2003;423:889–893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

