Unique distribution of aromatase in the human brain: in vivo studies with PET and [N-methyl-11C]vorozole
- PMID: 20842717
- PMCID: PMC2941230
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.20791
Unique distribution of aromatase in the human brain: in vivo studies with PET and [N-methyl-11C]vorozole
Abstract
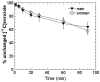
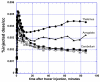
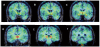
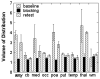
Aromatase catalyzes the last step in estrogen biosynthesis. Brain aromatase is involved in diverse neurophysiological and behavioral functions including sexual behavior, aggression, cognition, and neuroprotection. Using positron emission tomography (PET) with the radiolabeled aromatase inhibitor [N-methyl-(11)C]vorozole, we characterized the tracer distribution and kinetics in the living human brain. Six young, healthy subjects, three men and three women, were administered the radiotracer alone on two separate occasions. Women were scanned in distinct phases of the menstrual cycle. Specificity was confirmed by pretreatment with a pharmacological (2.5 mg) dose of the aromatase inhibitor letrozole. PET data were acquired over a 90-min period and regions of interest placed over selected brain regions. Brain and plasma time activity curves, corrected for metabolites, were used to derive kinetic parameters. Distribution volume (V(T)) values in both men and women followed the following rank order: thalamus > amygdala = preoptic area > medulla (inferior olive) > accumbens, pons, occipital and temporal cortex, putamen, cerebellum, and white matter. Pretreatment with letrozole reduced V(T) in all regions, though the size of the reduction was region-dependent, ranging from ∼70% blocking in thalamus andpreoptic area to ∼10% in cerebellum. The high levels of aromatase in thalamus and medulla (inferior olive) appear to be unique to humans. These studies set the stage for the noninvasive assessment of aromatase involvement in various physiological and pathological processes affecting the human brain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aromatase imaging with [N-methyl-11C]vorozole PET in healthy men and women.J Nucl Med. 2015 Apr;56(4):580-5. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.150383. Epub 2015 Feb 19. J Nucl Med. 2015. PMID: 25698781
-
In vivo imaging of brain aromatase in female baboons: [11C]vorozole kinetics and effect of the menstrual cycle.Mol Imaging. 2013 Nov-Dec;12(8). doi: 10.2310/7290.2013.00068. Mol Imaging. 2013. PMID: 24447618
-
Kinetic analysis of [11C]vorozole binding in the human brain with positron emission tomography.Mol Imaging. 2014;13:1-12. Mol Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24824855
-
In vivo visualization of aromatase in animals and humans.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2016 Jan;40:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26456904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pre-clinical and clinical review of vorozole, a new third generation aromatase inhibitor.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998;49 Suppl 1:S59-65; discussion S73-7. doi: 10.1023/a:1006052923468. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998. PMID: 9797019 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of aromatase expression in the adult male and female mouse brain. I. Coexistence with oestrogen receptors α and β, and androgen receptors.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 19;9(3):e90451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090451. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24646567 Free PMC article.
-
Prelimbic of Medial Prefrontal Cortex GABA Modulation through Testosterone on Spatial Learning and Memory.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Summer;18(3):1429-1444. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.1100745. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 32641952 Free PMC article.
-
Immunofluorescent Evidence for Nuclear Localization of Aromatase in Astrocytes in the Rat Central Nervous System.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 11;23(16):8946. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168946. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012212 Free PMC article.
-
Aromatase in the Human Brain.Androg Clin Res Ther. 2021 Dec 23;2(1):189-202. doi: 10.1089/andro.2021.0007. eCollection 2021. Androg Clin Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 35024691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addiction and Dopamine: Sex Differences and Insights from Studies of Smoking.Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2018 Oct;23:150-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2018. PMID: 30746429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelgadir SE, Resko JA, Ojeda SR, Lephart ED, McPhaul MJ, Roselli CE. Androgens regulate aromatase cytochrome P450 messenger ribonucleic acid in rat brain. Endocrinology. 1994;135:395–401. - PubMed
-
- Alexoff DL, Shea C, Wolf AP, Fowler JS, King P, Gatley SJ, Schlyer DJ. Plasma Input Function Determination for PET Using a Commercial Laboratory Robot. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1995;22:893–904. - PubMed
-
- Brailoiu E, Dun SL, Brailoiu GC, Mizuo K, Sklar LA, Oprea TI, Prossnitz ER, Dun NJ. Distribution and characterization of estrogen receptor G protein-coupled receptor 30 in the rat central nervous system. J Endocrinol. 2007;193:311–321. - PubMed
-
- Budzar A, Howell A. Advances in aromatase inhibition: Clinical efficacy and tolerability in the treatment of breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:2620–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
